2024-08-07 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-new-ai-approach-to-protein-design/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50571-y
タンパク質配列設計のためのコンテキストを考慮した幾何学的ディープラーニング Context-aware geometric deep learning for protein sequence design
Lucien F. Krapp,Fernando A. Meireles,Luciano A. Abriata,Jean Devillard,Sarah Vacle,Maria J. Marcaida &Matteo Dal Peraro
Nature Communications Published::25 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50571-y
Abstract
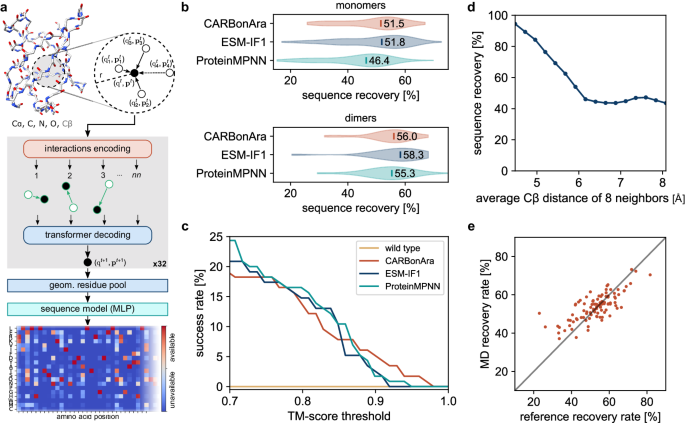
Protein design and engineering are evolving at an unprecedented pace leveraging the advances in deep learning. Current models nonetheless cannot natively consider non-protein entities within the design process. Here, we introduce a deep learning approach based solely on a geometric transformer of atomic coordinates and element names that predicts protein sequences from backbone scaffolds aware of the restraints imposed by diverse molecular environments. To validate the method, we show that it can produce highly thermostable, catalytically active enzymes with high success rates. This concept is anticipated to improve the versatility of protein design pipelines for crafting desired functions.