20024-08-15 カーディフ大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/news/view/2835386-perimenopause-linked-with-increased-risk-of-mania-and-manic-depression
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44220-024-00292-4
更年期における躁病、統合失調症スペクトラム障害、大うつ病性障害の初発の検討 Exploration of first onsets of mania, schizophrenia spectrum disorders and major depressive disorder in perimenopause
Lisa M. Shitomi-Jones,Clare Dolman,Ian Jones,George Kirov,Valentina Escott-Price,Sophie E. Legge & Arianna Di Florio
Nature Mental Health Published:15 August 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-024-00292-4
Abstract
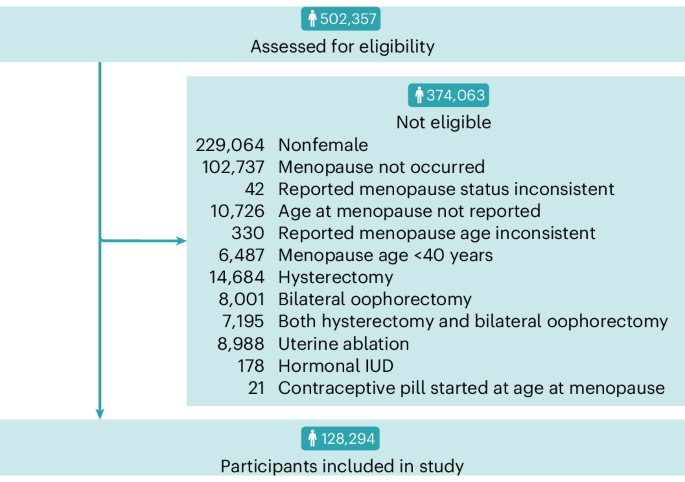
Although the relationship between perimenopause and changes in mood has been well established, knowledge of risk of a broad spectrum of psychiatric disorders associated with reproductive aging is limited. Here we investigate whether the perimenopause (that is, the years around the final menstrual period (FMP)) is associated with increased risk of developing psychiatric disorders compared with the late reproductive stage. Information on menopausal timing and psychiatric history was obtained from nurse-administered interviews and online questionnaires from 128,294 female participants within UK Biobank. Incidence rates of psychiatric disorders during the perimenopause (4 years surrounding the FMP) were compared with the reference premenopausal period (6–10 years before the FMP). The rates were calculated for major depressive disorder (MDD), mania, schizophrenia spectrum disorders and other diagnoses. Overall, of 128,294 participants, 753 (0.59%) reported their first onset of a psychiatric disorder during the late reproductive stage (incidence rate 1.53 per 1,000 person-years) and 1,133 (0.88%) during the perimenopause (incidence rate 2.33 per 1,000 person-years). Compared with the reference reproductive period, incidence rates of psychiatric disorders significantly increased during the perimenopause (incidence rate ratio (RR) of 1.52, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.39–1.67) and decreased back down to that observed in the premenopausal period in the postmenopause (RR of 1.09 (95% CI 0.98–1.21)). The effect was primarily driven by increased incidence rates of MDD, with an incidence RR of 1.30 (95% CI 1.16–1.45). However, the largest effect size at perimenopause was observed for mania (RR of 2.12 (95% CI 1.30–3.52)). No association was found between perimenopause and incidence rates of schizophrenia spectrum disorders (RR of 0.95 (95% CI 0.48–1.88)). In conclusion, perimenopause was associated with an increased risk of developing MDD and mania. No association was found between perimenopause and first onsets of schizophrenia spectrum disorders.