2024-09-26 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/unexpected-immune-response-may-hold-key-to-long–2/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07762-w
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07962-4
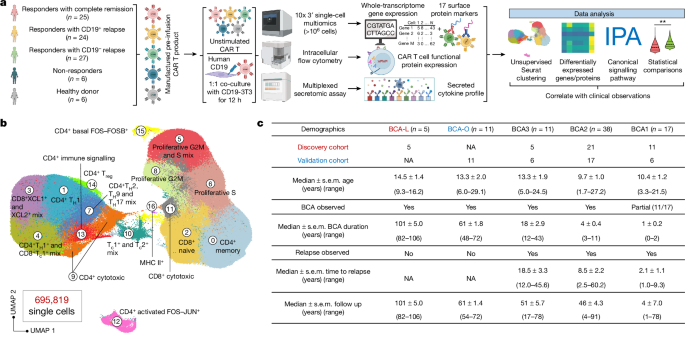
単一細胞CAR Tアトラスが8年間の白血病寛解におけるタイプ2の機能を明らかにする Single-cell CAR T atlas reveals type 2 function in 8-year leukaemia remission
Zhiliang Bai,Bing Feng,Susan E. McClory,Beatriz Coutinho de Oliveira,Caroline Diorio,Céline Gregoire,Bo Tao,Luojia Yang,Ziran Zhao,Lei Peng,Giacomo Sferruzza,Liqun Zhou,Xiaolei Zhou,Jessica Kerr,Alev Baysoy,Graham Su,Mingyu Yang,Pablo G. Camara,Sidi Chen,Li Tang,Carl H. June,J. Joseph Melenhorst,Stephan A. Grupp & Rong Fan
Nature Published:25 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07762-w
Abstract
Despite a high response rate in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy for acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL)1,2,3, approximately 50% of patients relapse within the first year4,5,6, representing an urgent question to address in the next stage of cellular immunotherapy. Here, to investigate the molecular determinants of ultralong CAR T cell persistence, we obtained a single-cell multi-omics atlas from 695,819 pre-infusion CAR T cells at the basal level or after CAR-specific stimulation from 82 paediatric patients with ALL enrolled in the first two CAR T ALL clinical trials and 6 healthy donors. We identified that elevated type 2 functionality in CAR T infusion products is significantly associated with patients maintaining a median B cell aplasia duration of 8.4 years. Analysis of ligand–receptor interactions revealed that type 2 cells regulate a dysfunctional subset to maintain whole-population homeostasis, and the addition of IL-4 during antigen-specific activation alleviates CAR T cell dysfunction while enhancing fitness at both transcriptomic and epigenomic levels. Serial proteomic profiling of sera after treatment revealed a higher level of circulating type 2 cytokines in 5-year or 8-year relapse-free responders. In a leukaemic mouse model, type 2high CAR T cell products demonstrated superior expansion and antitumour activity, particularly after leukaemia rechallenge. Restoring antitumour efficacy in type 2low CAR T cells was attainable by enhancing their type 2 functionality, either through incorporating IL-4 into the manufacturing process or by priming manufactured CAR T products with IL-4 before infusion. Our findings provide insights into the mediators of durable CAR T therapy response and suggest potential therapeutic strategies to sustain long-term remission by boosting type 2 functionality in CAR T cells.
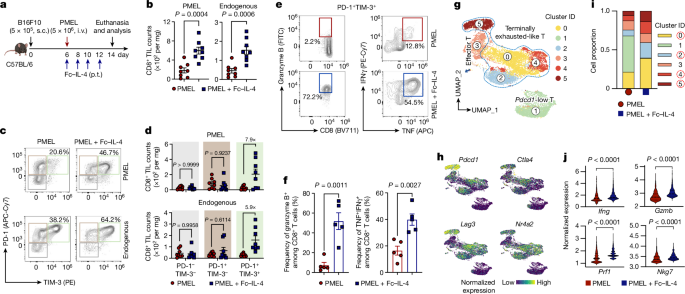
2型サイトカインFc-IL-4ががんに対する疲弊したCD8+T細胞を活性化する The type 2 cytokine Fc–IL-4 revitalizes exhausted CD8+ T cells against cancer
Bing Feng,Zhiliang Bai,Xiaolei Zhou,Yang Zhao,Yu-Qing Xie,Xinyi Huang,Yang Liu,Tom Enbar,Rongrong Li,Yi Wang,Min Gao,Lucia Bonati,Mei-Wen Peng,Weilin Li,Bo Tao,Mélanie Charmoy,Werner Held,J. Joseph Melenhorst,Rong Fan,Yugang Guo & Li Tang
Nature Published:25 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07962-4
Abstract
Current cancer immunotherapy predominately focuses on eliciting type 1 immune responses fighting cancer; however, long-term complete remission remains uncommon1,2. A pivotal question arises as to whether type 2 immunity can be orchestrated alongside type 1-centric immunotherapy to achieve enduring response against cancer3,4. Here we show that an interleukin-4 fusion protein (Fc–IL-4), a typical type 2 cytokine, directly acts on CD8+ T cells and enriches functional terminally exhausted CD8+ T (CD8+ TTE) cells in the tumour. Consequently, Fc–IL-4 enhances antitumour efficacy of type 1 immunity-centric adoptive T cell transfer or immune checkpoint blockade therapies and induces durable remission across several syngeneic and xenograft tumour models. Mechanistically, we discovered that Fc–IL-4 signals through both signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways, augmenting the glycolytic metabolism and the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) concentration of CD8+ TTE cells in a lactate dehydrogenase A-dependent manner. The metabolic modulation mediated by Fc–IL-4 is indispensable for reinvigorating intratumoural CD8+ TTE cells. These findings underscore Fc–IL-4 as a potent type 2 cytokine-based immunotherapy that synergizes effectively with type 1 immunity to elicit long-lasting responses against cancer. Our study not only sheds light on the synergy between these two types of immune responses, but also unveils an innovative strategy for advancing next-generation cancer immunotherapy by integrating type 2 immune factors.