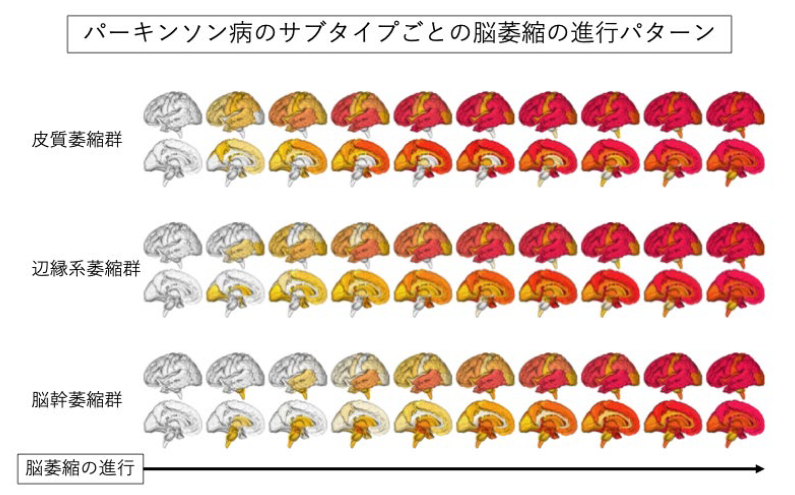
2024-10-24 カリフォルニア大学サンタバーバラ校(UCSB)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucsb.edu/2024/021657/researchers-complete-largest-compilation-cancer-prevalence-across-vertebrates
- https://aacrjournals.org/cancerdiscovery/article/doi/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0573/749321/Cancer-Prevalence-across-VertebratesCancer-across
脊椎動物全体のがん有病率 Cancer Prevalence across Vertebrates
Zachary T. Compton;Walker Mellon;Valerie K. Harris;Shawn Rupp;Diego Mallo;Stefania E. Kapsetaki;Mallory Wilmot;Ryan Kennington;Kathleen Noble;Cristina Baciu;Lucia N. Ramirez;Ashley Peraza;Brian Martins;Sushil Sudhakar;Selin Aksoy;Gabriela Furukawa;Orsolya Vincze;Mathieu Giraudeau;Elizabeth G. Duke;Simon Spiro;Edmund Flach;Hannah Davidson;Christopher I. Li;Ashley Zehnder;Trevor A. Graham;Brigid V. Troan;Tara M. Harrison;Marc Tollis;Joshua D. Schiffman;C. Athena Aktipis;Lisa M. Abegglen;Carlo C. Maley;Amy M. Boddy
Cancer Discovery Published:October 24 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0573
Abstract
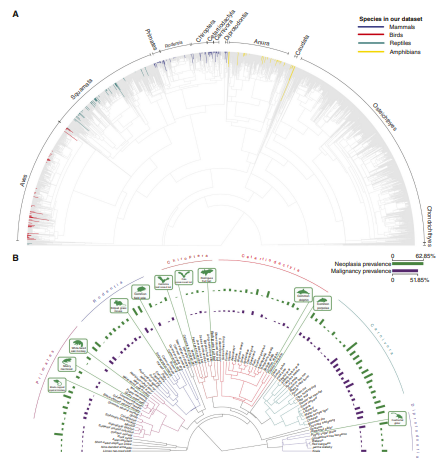
Cancer is pervasive across multicellular species, but what explains the differences in cancer prevalence across species? Using 16,049 necropsy records for 292 species spanning three clades of tetrapods (amphibians, sauropsids, and mammals), we found that neoplasia and malignancy prevalence increases with adult mass (contrary to Peto’s paradox) and somatic mutation rate but decreases with gestation time. The relationship between adult mass and malignancy prevalence was only apparent when we controlled for gestation time. Evolution of cancer susceptibility appears to have undergone sudden shifts followed by stabilizing selection. Outliers for neoplasia prevalence include the common porpoise (<1.3%), the Rodrigues fruit bat (<1.6%), the black-footed penguin (<0.4%), ferrets (63%), and opossums (35%). Discovering why some species have particularly high or low levels of cancer may lead to a better understanding of cancer syndromes and novel strategies for the management and prevention of cancer.
Significance: Evolution has discovered mechanisms for suppressing cancer in a wide variety of species. By analyzing veterinary necropsy records, we can identify species with exceptionally high or low cancer prevalence. Discovering the mechanisms of cancer susceptibility and resistance may help improve cancer prevention and explain cancer syndromes.