2024-10-25 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/heatwaves-and-an-aging-population-increase-the-risk-of-severe-electrolyte-imbalances
- https://journals.lww.com/jasn/fulltext/9900/the_association_of_outdoor_temperature_with_severe.435.aspx
屋外の気温と重症低ナトリウム血症との関連性 The Association of Outdoor Temperature with Severe Hyponatremia
Issa, Issa; Skov, Jakob; Falhammar, Henrik; Lindh, Jonatan D.; Mannheimer, Buster
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology Published:October 14, 2024
DOI:10.1681/ASN.0000000519
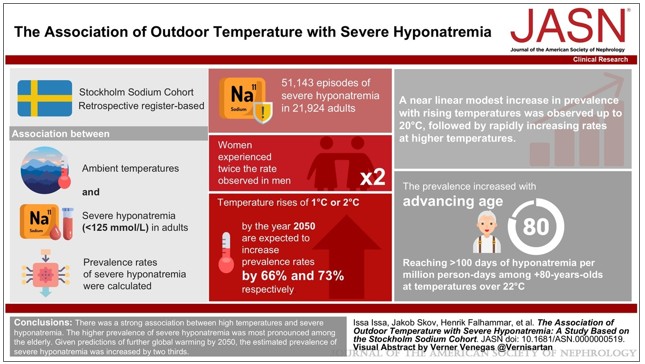
Visual Abstract
Abstract
Key Points
- High temperature is associated with severe hyponatremia.
- The association between outdoor temperature and severe hyponatremia is most pronounced among women and elderly individuals.
- Given the predictions of further global warming and demographic changes by 2050, the estimated prevalence of severe hyponatremia may increase by 66%.
Background
Hyponatremia is a common condition with nonspecific symptoms and a complicated etiology. The association of outdoor temperature on hyponatremia is not well studied and varies depending on the climate and location. This study aimed to investigate the association between outdoor temperature and the prevalence of severe hyponatremia.
Methods
This retrospective register-based cohort study based on the Stockholm Sodium Cohort investigated the association between ambient temperatures and severe hyponatremia (<125 mmol/L) in adults. Prevalence rates of severe hyponatremia were calculated as the number of days of severe hyponatremia divided by person-days at risk for the same temperature, using mean daily temperatures at the area of residence of each study participant to calculate exposure time. A prediction model incorporating changes in demographics and climate was used to estimate the burden of severe hyponatremia in Stockholm by 2050.
Results
We identified 51,143 episodes of severe hyponatremia in 21,924 adults. A near linear modest increase in prevalence with rising temperatures was observed up to 20°C, followed by rapidly increasing rates at higher temperatures. The prevalence was higher with older age, reaching >100 days of hyponatremia per million person-days among those older than 80 years at temperatures over 22°C. Women experienced twice the rate observed in men. Temperature rises of 1°C or 2°C by the year 2050 are expected to be associated with higher prevalence rates by 66% and 73%, respectively.
Conclusions
There was a strong association between high temperatures and severe hyponatremia. The higher prevalence of severe hyponatremia was most pronounced among elderly individuals.