2024-11-15 タフツ大学
<関連情報>
- https://now.tufts.edu/2024/11/15/researcher-targets-dna-repair-vulnerabilities-female-reproductive-cancers
- https://academic.oup.com/narmolmed/article/1/4/ugae010/7789841
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51595-0
原発性卵巣機能不全、子宮内膜症、多嚢胞性卵巣症候群におけるRAD51制御因子および変異体の役割 The role of RAD51 regulators and variants in primary ovarian insufficiency, endometriosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome
Maggie Witham, Sarah R Hengel
NAR Molecular Medicine Published:28 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/narmme/ugae010

Graphical Abstract
Abstract
The study of RAD51 regulators in female reproductive diseases has novel biomarker potential and implications for therapeutic advancement. Regulators of RAD51 play important roles in maintaining genome integrity and variations in these genes have been identified in female reproductive diseases including primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), endometriosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). RAD51 modulators change RAD51 activity in homologous recombination, replication stress, and template switching pathways. However, molecular implications of these proteins in primary ovarian insufficiency, endometriosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome have been understudied. For each reproductive disease, we provide its definition, current diagnostic and therapeutic treatment strategies, and associated genetic variations. Variants were discovered in RAD51, and regulators including DMC1, RAD51B, SWS1, SPIDR, XRCC2 and BRCA2 linked with POI. Endometriosis is associated with variants in XRCC3, BRCA1 and CSB genes. Variants in BRCA1 were associated with PCOS. Our analysis identified novel biomarkers for POI (DMC1 and RAD51B) and PCOS (BRCA1). Further biochemical and cellular analyses of RAD51 regulator functions in reproductive disorders will advance our understanding of the pathogenesis of these diseases.
ヒトShu複合体はssDNA上のRPA動態を調節することによりRAD51活性を促進する The human Shu complex promotes RAD51 activity by modulating RPA dynamics on ssDNA
Sarah R. Hengel,Katherine G. Oppenheimer,Chelsea M. Smith,Matthew A. Schaich,Hayley L. Rein,Julieta Martino,Kristie E. Darrah,Maggie Witham,Oluchi C. Ezekwenna,Kyle R. Burton,Bennett Van Houten,Maria Spies & Kara A. Bernstein
Nature Communications Published:21 August 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51595-0
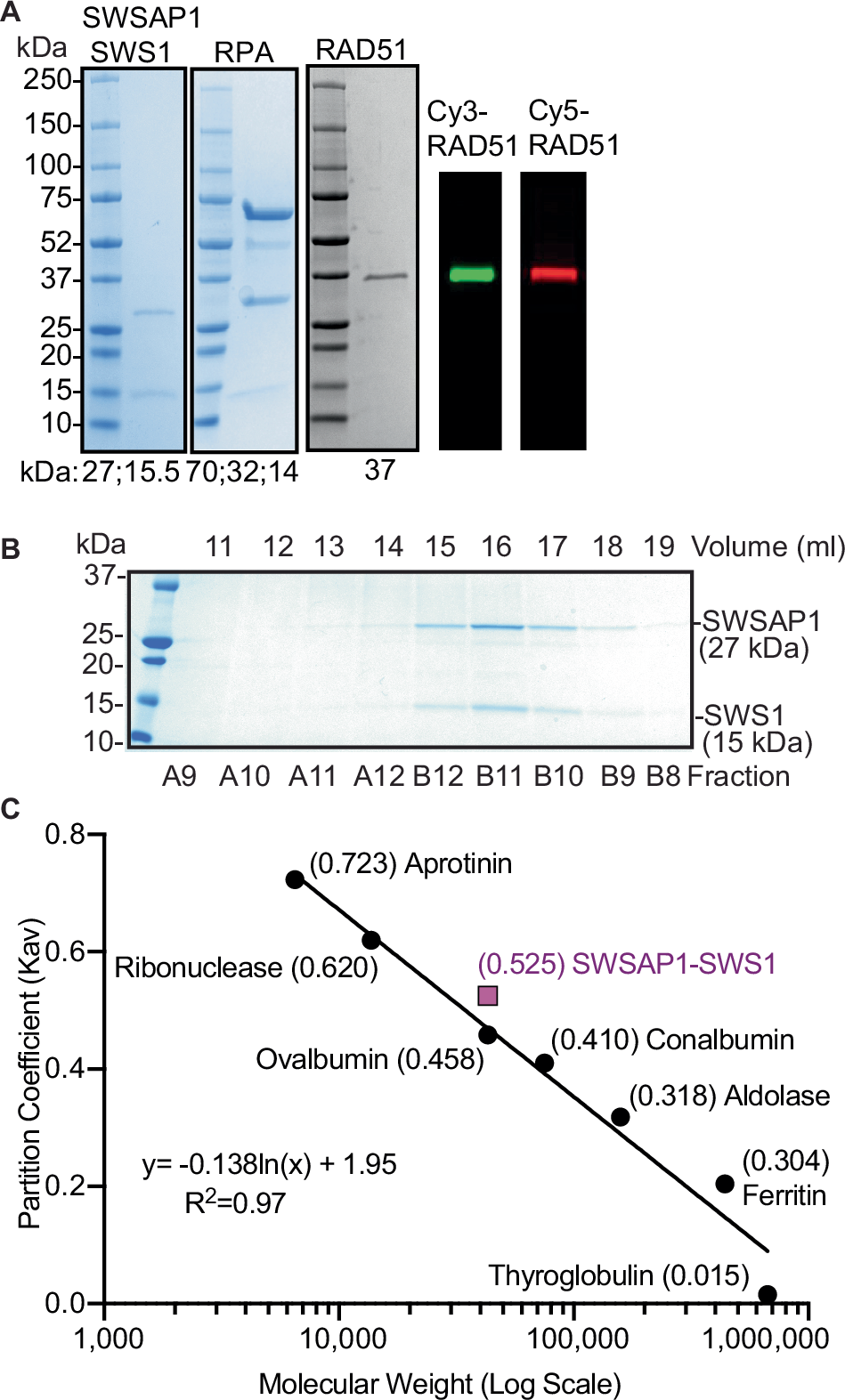
Abstract
Templated DNA repair that occurs during homologous recombination and replication stress relies on RAD51. RAD51 activity is positively regulated by BRCA2 and the RAD51 paralogs. The Shu complex is a RAD51 paralog-containing complex consisting of SWSAP1, SWS1, and SPIDR. We demonstrate that SWSAP1-SWS1 binds RAD51, maintains RAD51 filament stability, and enables strand exchange. Using single-molecule confocal fluorescence microscopy combined with optical tweezers, we show that SWSAP1-SWS1 decorates RAD51 filaments proficient for homologous recombination. We also find SWSAP1-SWS1 enhances RPA diffusion on ssDNA. Importantly, we show human sgSWSAP1 and sgSWS1 knockout cells are sensitive to pharmacological inhibition of PARP and APE1. Lastly, we identify cancer variants in SWSAP1 that alter Shu complex formation. Together, we show that SWSAP1-SWS1 stimulates RAD51-dependent high-fidelity repair and may be an important new cancer therapeutic target.