2024-12-06 インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン(ICL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/259073/new-ai-stroke-brain-scan-readings/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41746-024-01325-z
非強化CTから虚血性脳卒中病変の年代をディープラーニングでバイオマーカー化 Deep learning biomarker of chronometric and biological ischemic stroke lesion age from unenhanced CT
Adam Marcus,Grant Mair,Liang Chen,Charles Hallett,Claudia Ghezzou Cuervas-Mons,Dylan Roi,Daniel Rueckert & Paul Bentley
npj Digital Medicine Published:06 December 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-024-01325-z
Abstract
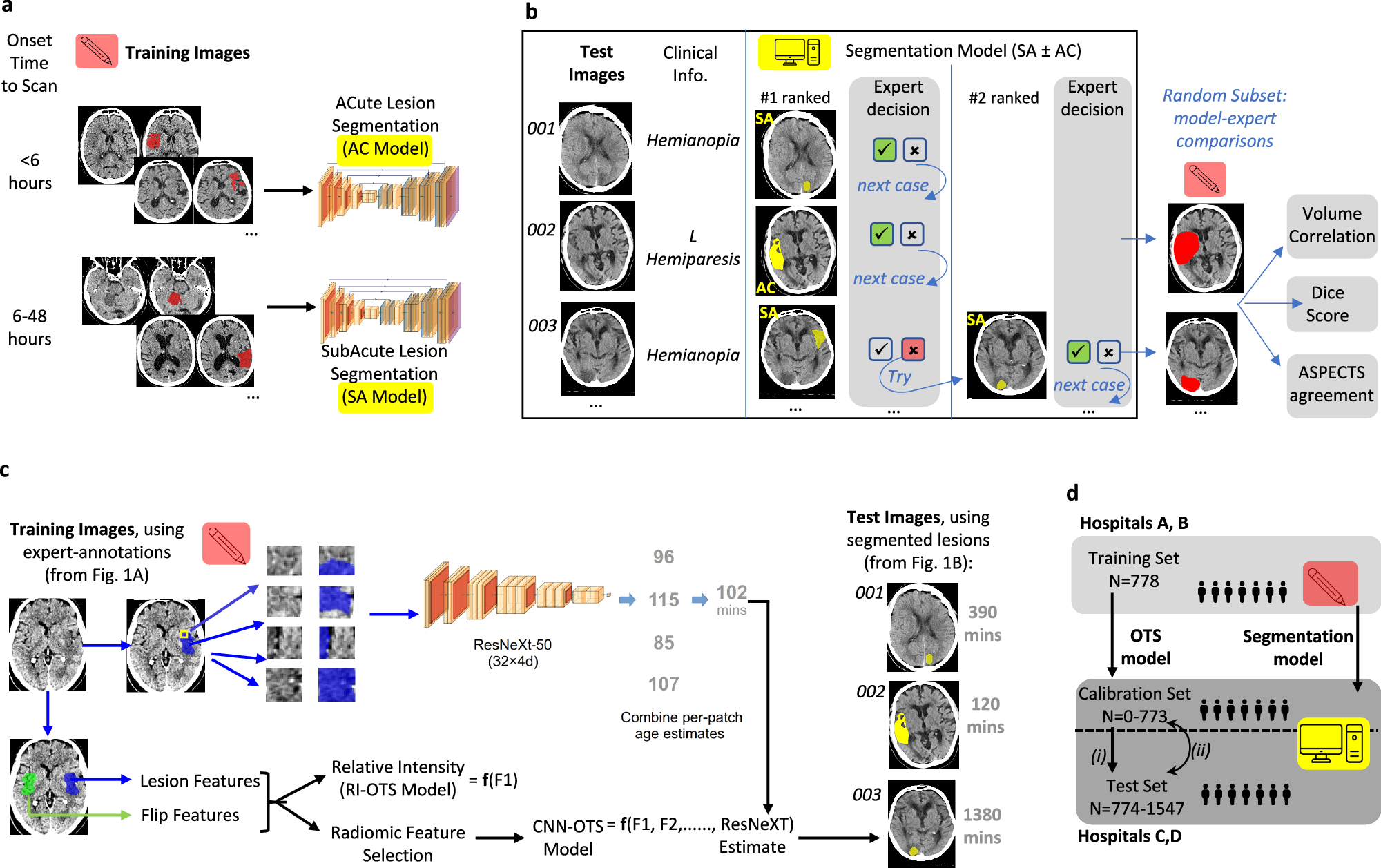
Estimating progression of acute ischemic brain lesions – or biological lesion age – holds huge practical importance for hyperacute stroke management. The current best method for determining lesion age from non-contrast computerised tomography (NCCT), measures Relative Intensity (RI), termed Net Water Uptake (NWU). We optimised lesion age estimation from NCCT using a convolutional neural network – radiomics (CNN-R) model trained upon chronometric lesion age (Onset Time to Scan: OTS), while validating against chronometric and biological lesion age in external datasets (N = 1945). Coefficients of determination (R2) for OTS prediction, using CNN-R, and RI models were 0.58 and 0.32 respectively; while CNN-R estimated OTS showed stronger associations with ischemic core:penumbra ratio, than RI and chronometric, OTS (ρ2 = 0.37, 0.19, 0.11); and with early lesion expansion (regression coefficients >2x for CNN-R versus others) (all comparisons: p < 0.05). Concluding, deep-learning analytics of NCCT lesions is approximately twice as accurate as NWU for estimating chronometric and biological lesion ages.