2023-05-25 ブラウン大学
◆研究では、マウスの脳内の血管の変化を長期間追跡できることが示されており、これにより生体医学の研究者たちは、アルツハイマー病、パーキンソン病、ハンチントン病、多発性硬化症などの進行性神経変性疾患の早期発見に関する重要な手掛かりを得ることができるかもしれません。
<関連情報>
- https://www.brown.edu/news/2023-05-25/vascular-tracking
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38609-z
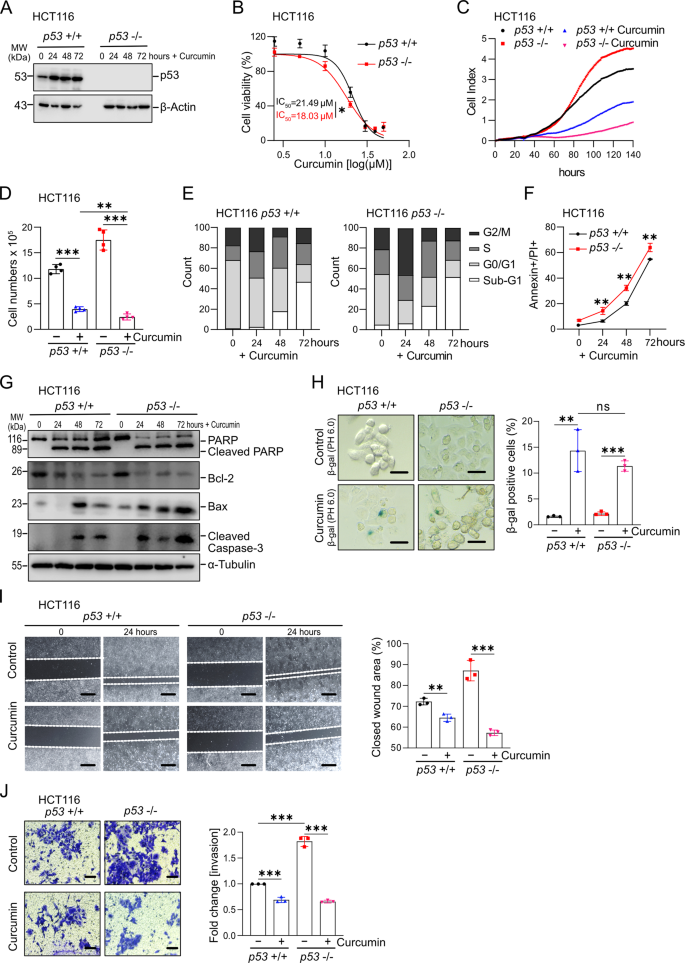
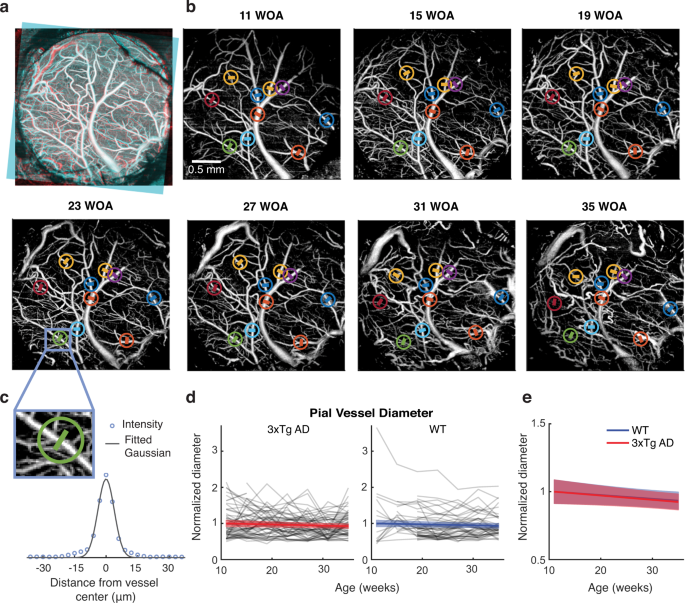
雄マウスにおける脳微小血管の形態、トポロジー、流れの寿命間近の縦断追跡 Near-lifespan longitudinal tracking of brain microvascular morphology, topology, and flow in male mice
Konrad W. Walek,Sabina Stefan,Jang-Hoon Lee,Pooja Puttigampala,Anna H. Kim,Seong Wook Park,Paul J. Marchand,Frederic Lesage,Tao Liu,Yu-Wen Alvin Huang,David A. Boas,Christopher Moore & Jonghwan Lee
Nature Communications Published:24 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38609-z
Abstract
In age-related neurodegenerative diseases, pathology often develops slowly across the lifespan. As one example, in diseases such as Alzheimer’s, vascular decline is believed to onset decades ahead of symptomology. However, challenges inherent in current microscopic methods make longitudinal tracking of such vascular decline difficult. Here, we describe a suite of methods for measuring brain vascular dynamics and anatomy in mice for over seven months in the same field of view. This approach is enabled by advances in optical coherence tomography (OCT) and image processing algorithms including deep learning. These integrated methods enabled us to simultaneously monitor distinct vascular properties spanning morphology, topology, and function of the microvasculature across all scales: large pial vessels, penetrating cortical vessels, and capillaries. We have demonstrated this technical capability in wild-type and 3xTg male mice. The capability will allow comprehensive and longitudinal study of a broad range of progressive vascular diseases, and normal aging, in key model systems.