2023-05-25 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
◆ドイツのLMU大学のHeiko Hermeking教授率いるチームは、スパイスのウコンに含まれる天然物質であるクルクミンが、この防御機構を活性化させることでp53を補完することを細胞培養とマウスモデルで実証しました。この結果は新たな治療法の可能性を示唆しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/colon-cancer-curcumin-activates-tumor-suppressive-signaling-pathway.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-023-01178-1
クルクミンはROS/KEAP1/NRF2/miR-34a/b/cカスケードを活性化し、大腸がん転移を抑制する Curcumin activates a ROS/KEAP1/NRF2/miR-34a/b/c cascade to suppress colorectal cancer metastasis
Chunfeng Liu,Matjaz Rokavec,Zekai Huang & Heiko Hermeking
Cell Death & Differentiation Published:20 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-023-01178-1
Abstract
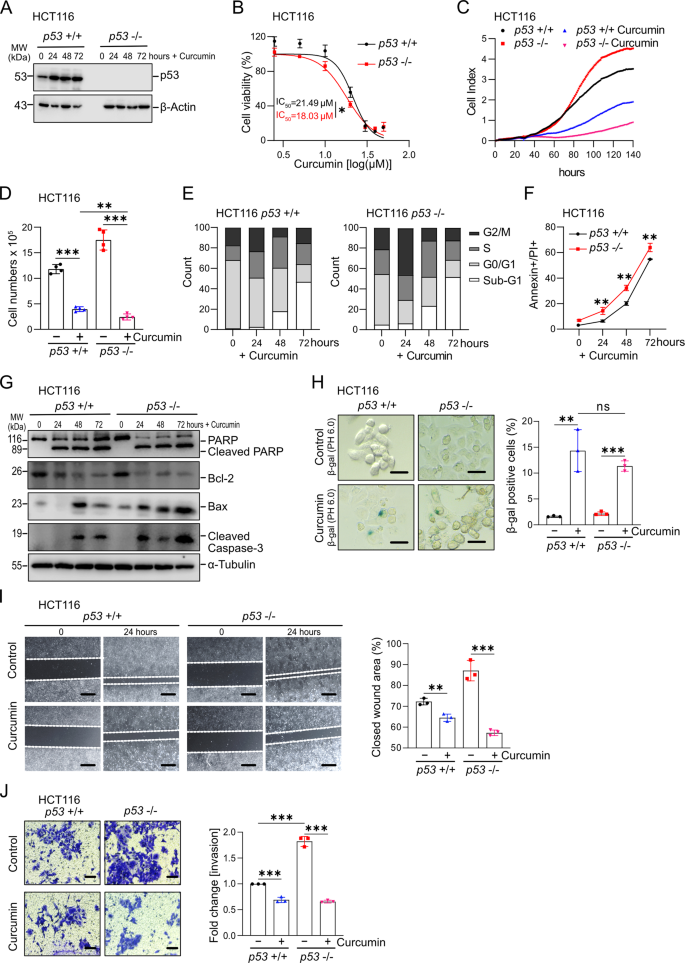
Curcumin, a natural phytochemical isolated from tumeric roots, represents a candidate for prevention and therapy of colorectal cancer/CRC. However, the exact mechanism of action and the downstream mediators of curcumin’s tumor suppressive effects have remained largely unknown. Here we used a genetic approach to determine the role of the p53/miR-34 pathway as mediator of the effects of curcumin. Three isogenic CRC cell lines rendered deficient for the p53, miR-34a and/or miR-34b/c genes were exposed to curcumin and subjected to cell biological analyses. siRNA-mediated inhibition and ectopic expression of NRF2, as well as Western blot, qPCR and qChIP analyses of its target genes were performed. CRC cells were i.v. injected into NOD/SCID mice and lung-metastases formation was determined by longitudinal, non-invasive imaging. In CRC cells curcumin induced apoptosis and senescence, and suppressed migration and invasion in a p53-independent manner. Curcumin activated the KEAP1/NRF2/ARE pathway by inducing ROS. Notably, curcumin induced miR-34a and miR-34b/c expression in a ROS/NRF2-dependent and p53-independent manner. NRF2 directly induced miR-34a and miR-34b/c via occupying multiple ARE motifs in their promoter regions. Curcumin reverted repression of miR-34a and miR-34b/c induced by IL6 and hypoxia. Deletion of miR-34a and miR-34b/c significantly reduced curcumin-induced apoptosis and senescence, and prevented the inhibition of migration and invasion by curcumin or ectopic NRF2. In CRC cells curcumin induced MET and prevented the formation of lung-metastases in mice in a miR-34a-dependent manner. In addition, we found that curcumin may enhance the therapeutic effects of 5-FU on CRC cells deficient for p53 and miR-34a/b/c. Activation of the KEAP1/NRF2/miR-34a/b/c axis mediates the tumor suppressive activity of curcumin and suggests a new approach for activating miR-34 genes in tumors for therapeutic purposes.