2025-01-06 タフツ大学
<関連情報>
- https://now.tufts.edu/2025/01/06/new-study-links-millions-diabetes-and-heart-disease-cases-globally-sugary-drinks
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03345-4
184カ国における砂糖入り飲料に起因する2型糖尿病と心血管疾患の負荷 Burdens of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease attributable to sugar-sweetened beverages in 184 countries
Laura Lara-Castor,Meghan O’Hearn,Frederick Cudhea,Victoria Miller,Peilin Shi,Jianyi Zhang,Julia R. Sharib,Sean B. Cash,Simon Barquera,Renata Micha,Dariush Mozaffarian & Global Dietary Database
Nature Medicine Published:06 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03345-4
Abstract
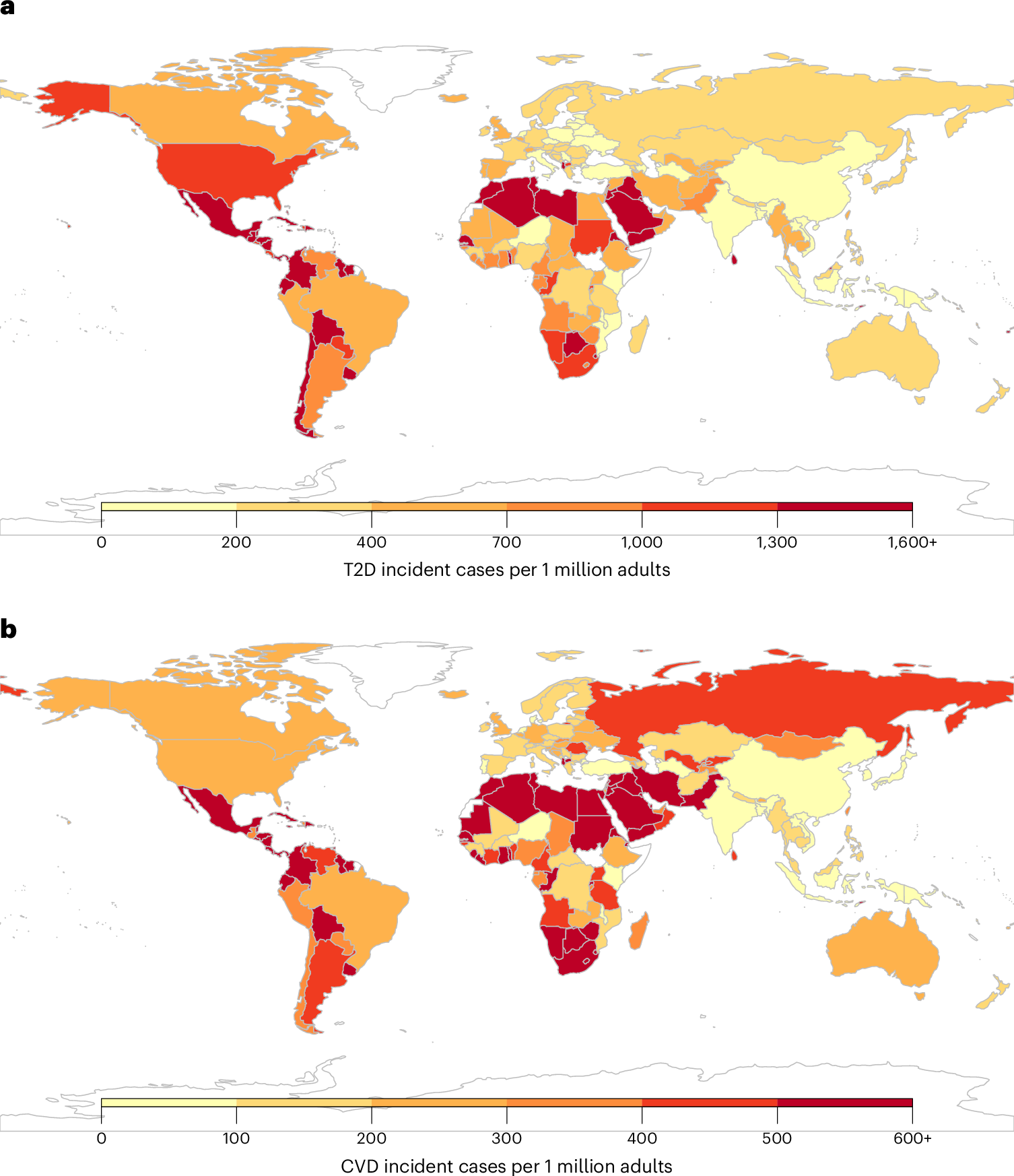
The consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) is associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). However, an updated and comprehensive assessment of the global burden attributable to SSBs remains scarce. Here we estimated SSB-attributable T2D and CVD burdens across 184 countries in 1990 and 2020 globally, regionally and nationally, incorporating data from the Global Dietary Database, jointly stratified by age, sex, educational attainment and urbanicity. In 2020, 2.2 million (95% uncertainty interval 2.0–2.3) new T2D cases and 1.2 million (95% uncertainty interval 1.1–1.3) new CVD cases were attributable to SSBs worldwide, representing 9.8% and 3.1%, respectively, of all incident cases. Globally, proportional SSB-attributable burdens were higher among men versus women, younger versus older adults, higher- versus lower-educated adults, and adults in urban versus rural areas. By world region, the highest SSB-attributable percentage burdens were in Latin America and the Caribbean (T2D: 24.4%; CVD: 11.3%) and sub-Saharan Africa (T2D: 21.5%; CVD: 10.5%). From 1990 to 2020, the largest proportional increases in SSB-attributable incident T2D and CVD cases were in sub-Saharan Africa (+8.8% and +4.4%, respectively). Our study highlights the countries and subpopulations most affected by cardiometabolic disease associated with SSB consumption, assisting in shaping effective policies and interventions to reduce these burdens globally.