2025-01-31 バーミンガム大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/news/2025/healthy-gut-bacteria-that-feed-on-sugar-analysed-for-the-first-time
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01911-7
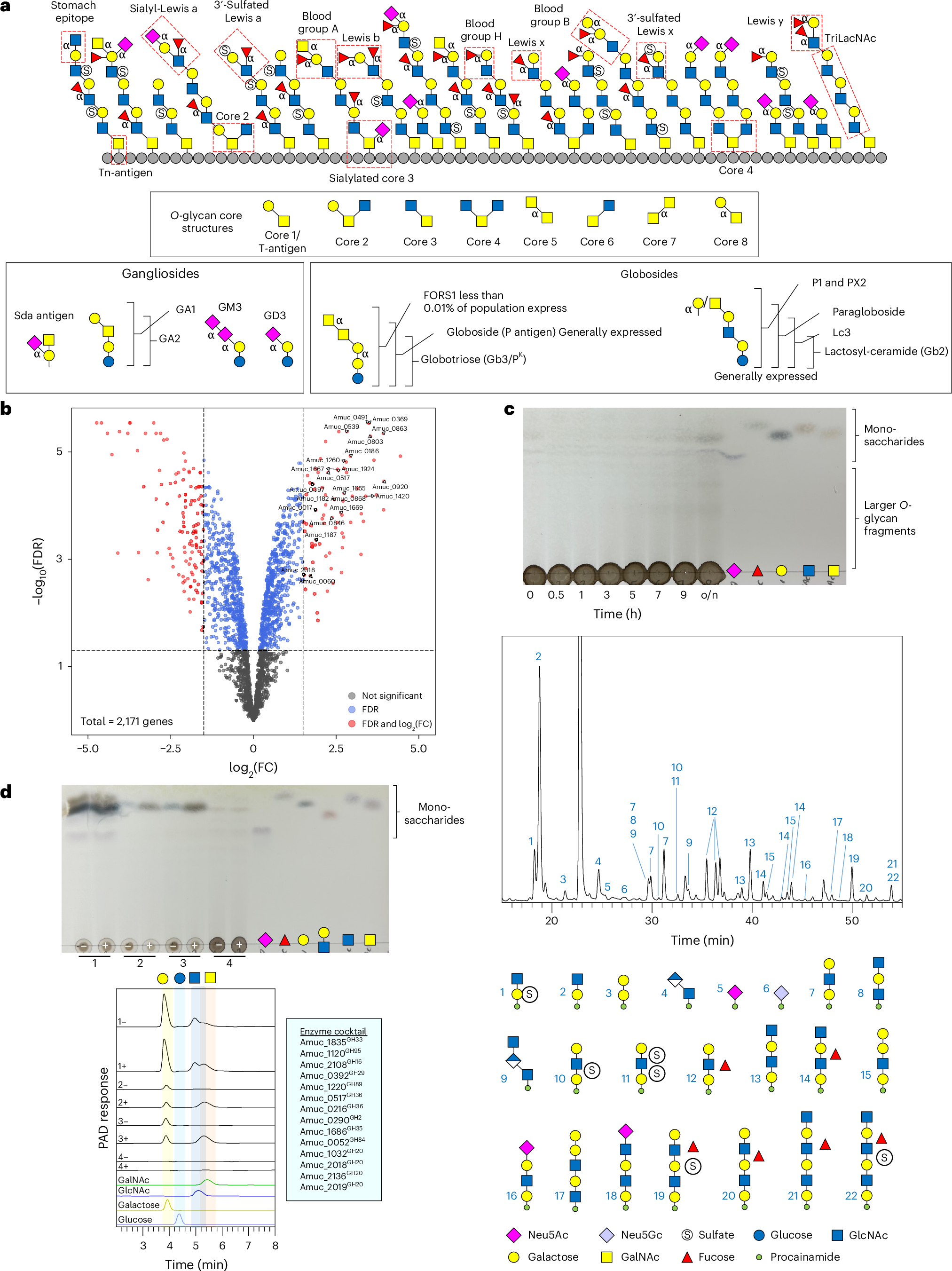
アッカーマンシア(Akkermansia muciniphila)の糖質活性酵素がムチンのO-糖鎖を分解して完成させる Carbohydrate-active enzymes from Akkermansia muciniphila break down mucin O-glycans to completion
Cassie R. Bakshani,Taiwo O. Ojuri,Bo Pilgaard,Jesper Holck,Ross McInnes,Radoslaw P. Kozak,Maria Zakhour,Sara Çakaj,Manon Kerouedan,Emily Newton,David N. Bolam & Lucy I. Crouch
Nature Microbiology Published:31 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-024-01911-7
Abstract
Akkermansia muciniphila is a human microbial symbiont residing in the mucosal layer of the large intestine. Its main carbon source is the highly heterogeneous mucin glycoprotein, and it uses an array of carbohydrate-active enzymes and sulfatases to access this complex energy source. Here we describe the biochemical characterization of 54 glycoside hydrolases, 11 sulfatases and 1 polysaccharide lyase from A. muciniphila to provide a holistic understanding of their carbohydrate-degrading activities. This was achieved using a variety of liquid chromatography techniques, mass spectrometry, enzyme kinetics and thin-layer chromatography. These results are supported with A. muciniphila growth and whole-cell assays. We find that these enzymes can act synergistically to degrade the O-glycans on the mucin polypeptide to completion, down to the core N-acetylgalactosaime. In addition, these enzymes can break down human breast milk oligosaccharide, ganglioside and globoside glycan structures, showing their capacity to target a variety of host glycans. These data provide a resource to understand the full degradative capability of the gut microbiome member A. muciniphila.


