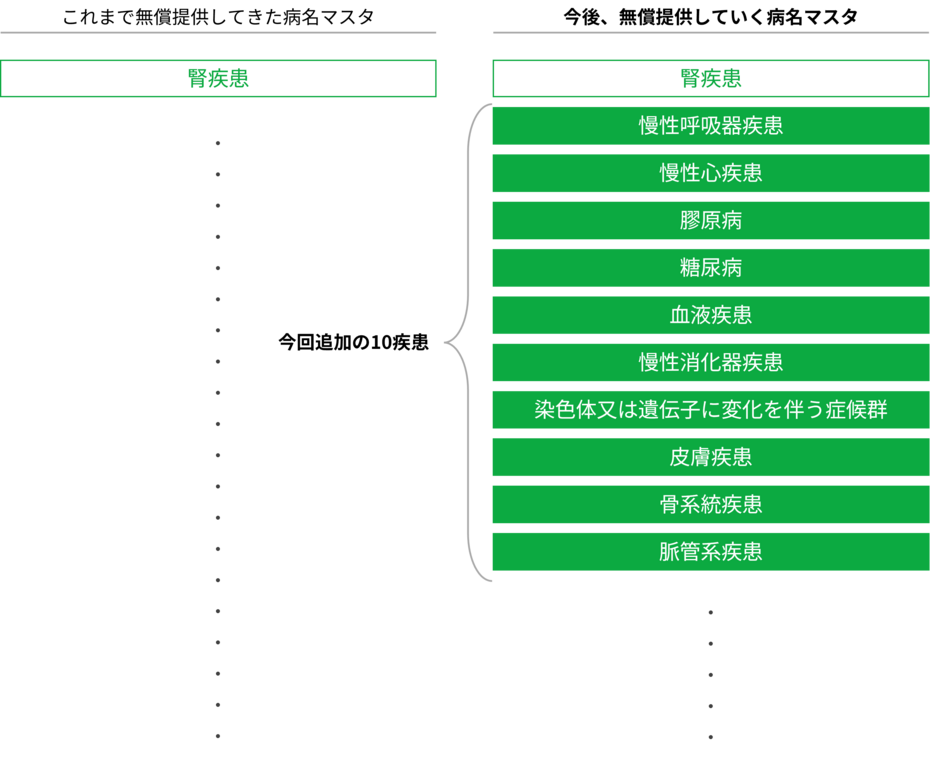
2025-03-19 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202503/t20250314_905543.shtml
- https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2417253122
シロイヌナズナの脱メチル化酵素REF6はphyBと物理的に相互作用し、赤色光下での胚軸伸長を促進する The Arabidopsis demethylase REF6 physically interacts with phyB to promote hypocotyl elongation under red light
Yan Yan, Jiaping Zhu, Qi Qiu, +2 , and Xian Deng
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Published:March 10, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2417253122
Significance
Photomorphogenesis, a key stage in early seedling growth exposed to light, is mediated by the photoreceptors. The dynamic trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys27 (H3K27me3) modulates gene expression and governs plant development and responses to the environmental changes. However, how chromatin and histone modifications respond to light signals remains largely obscure. This study uncovers a critical role of the H3K27me3 demethylase RELATIVE OF EARLY FLOWERING 6 (REF6)/JMJ12 in regulating light-responsive hypocotyl elongation. REF6 is activated by light and interacts with phytochrome B (phyB) to modulate chromatin accessibility and expression of cell elongation-related genes. Our findings uncover a link between light signals and epigenetic regulation, offering valuable insights into understanding the complex interactions among phytochrome, epigenetic factors, and transcription factors.
Abstract
The plant photoreceptor phytochrome B (phyB) mediates the responses of plants to red (R) light. Trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys27 (H3K27me3) plays a crucial role in governing gene expression and controlling the response of plants to environmental changes. However, how dynamic H3K27me3 mediates plant response to R light is poorly understood. Here, we report that RELATIVE OF EARLY FLOWERING 6 (REF6), an H3K27me3 demethylase, promotes hypocotyl elongation under R light in Arabidopsis. Upon exposure to R light, REF6 preferentially interacts with the active Pfr form of phyB. Consequently, phyB enhances REF6 accumulation and its binding ability, which are necessary for inducing cell-elongation-related genes from open chromatin, ensuring normal plant growth under prolonged light exposure. Moreover, REF6 acts together with the phyB-PIF4 module to mediate light regulation of hypocotyl growth. These findings provide insights into the understanding of how phytochromes, epigenetic factors, and transcription factors coordinately control plant growth in response to changing light environment.