2025-03-20 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/cell-atlas-of-the-endometrium-in-women-with-pcos-may-lead-to-better-treatment
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-03592-z
多嚢胞性卵巣症候群におけるヒト子宮内膜の単一細胞プロファイリング Single-cell profiling of the human endometrium in polycystic ovary syndrome
Gustaw Eriksson,Congru Li,Tina Gorsek Sparovec,Anja Dekanski,Sara Torstensson,Sanjiv Risal,Claes Ohlsson,Angelica Lindén Hirschberg,Sophie Petropoulos,Qiaolin Deng & Elisabet Stener-Victorin
Nature Medicine Published:20 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03592-z
Abstract
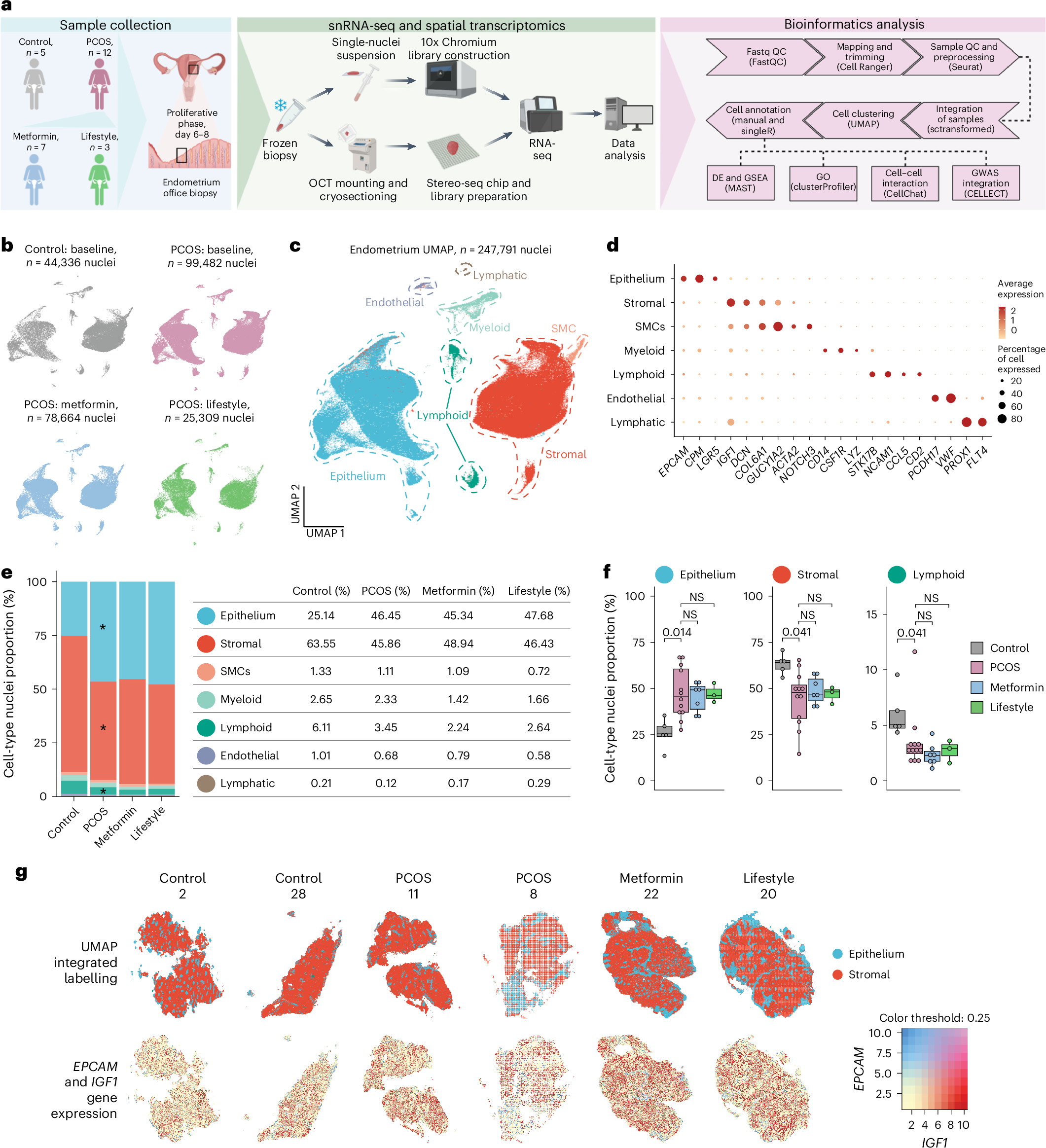
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) has a negative effect on the receptivity of the endometrium to embryo implantation and increases the risk of miscarriage and endometrial cancer. The cellular and molecular heterogeneity of the endometrium in women with PCOS has not been well studied. Our study presents a comprehensive cellular atlas of the endometrium during the proliferative phase in women with PCOS characterized by overweight and obesity, hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance compared with controls of similar age, weight and body mass index. Analysis of 247,791 isolated endometrial nuclei from 27 biopsies (5 controls and 12 PCOS cases at baseline and 7 after 16 weeks of metformin and 3 after lifestyle intervention) revealed cell-type-specific disease signatures and variations in cellular composition and localization. Samples taken after 16 weeks of metformin treatment and lifestyle management showed extensive recovery of disease-specific endometrial signatures. We linked the specific role of each cell type to clinical features such as hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance, and specific cell types to risk of endometrial and metabolic disease. In addition, potential therapeutic targets such as integrin inhibitors were identified and the role of metformin in restoring endometrial health in patients with PCOS was highlighted. Our findings lay the groundwork to significantly advance the understanding of PCOS-specific endometrial dysfunction for future targeted therapies.


