2025-03-21 マウントサイナイ医療システム (MSHS)
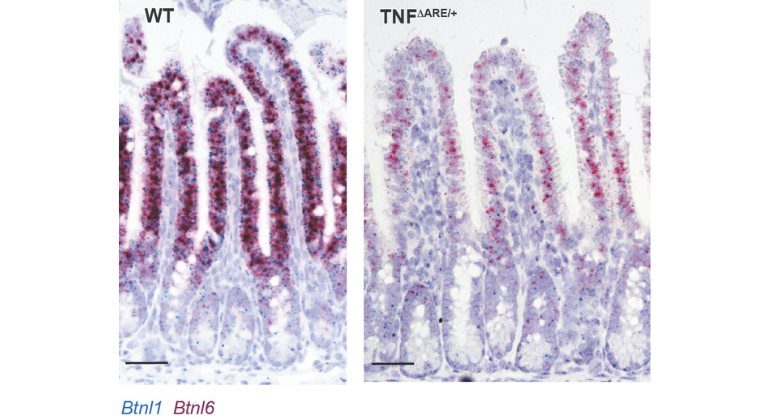
The expression of epithelial butyrophilin 1 and 6 (Btnl), which helps maintain T cells found within the intestinal epithelium, is decreased weeks before the onset of inflammation in a model of Crohn’s disease-like ileitis. Photo courtesy of Science Immunology
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/mount-sinai-led-team-identifies-cellular-mechanisms-that-may-lead-to-onset-of-inflammatory-bowel-disease
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.adk7429
γδ上皮内リンパ球の調節異常がクローン病様回腸炎に先行する Dysregulation of γδ intraepithelial lymphocytes precedes Crohn’s disease–like ileitis
Weili Xu, Natasha B. Golovchenko, Irving U. Martínez-Vargas, Andrew Fong, […], and Karen L. Edelblum
Science Immunology Published:21 Mar 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.adk7429
Editor’s summary
Although substantial progress has been made in identifying key risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease, the initiating events leading to the disease remain poorly understood. Using mouse models that spontaneously develop inflammation of the ileum, Xu et al. found that immunoregulatory ileal γδ intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) were reduced before the onset of chronic inflammation. Loss of ileal γδ IELs coincided with impaired immunosurveillance of the intestinal epithelium and infiltration of less mature peripheral γδ IELs. Together, these findings demonstrate that dysregulation of immunoregulatory γδ IELs could contribute to the initiation of Crohn’s disease. —Claire Olingy
Abstract
Intraepithelial lymphocytes expressing the γδ T cell receptor (γδ IELs) provide immunosurveillance of the intestinal barrier but are reduced in patients with active Crohn’s disease (CD). Here, we report an underappreciated role for γδ IELs in maintaining immunological tolerance during the onset and progression of CD-like ileitis using TNFΔARE/+ mice. We found that TNF-induced down-regulation of epithelial hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-gamma/butyrophilin is followed by a loss of ileal Vγ7 IELs and impaired barrier surveillance before the histological onset of disease. A reduction of immunoregulatory CD39+ γδ IELs coincided with the influx of immature, peripheral CD39neg γδ T cells into the epithelium, leading to an expansion of induced IELs, whereas an earlier depletion of γδ IELs correlated with accelerated onset of ileal inflammation. Our findings identify multiple layers of γδ IEL dysregulation before ileitis development, indicating that the loss of steady-state immunoregulatory γδ IELs may contribute to the initiation of ileal CD.