2025-04-02 カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2025/04/02/ai-effectively-predicts-dementia-risk-in-american-indian-alaska-native-elders/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11875197/#sec1
アメリカ・インディアンおよびアラスカ先住民の認知症を予測する機械学習:レトロスペクティブ・コホート研究 Machine learning to predict dementia for American Indian and Alaska native peoples: a retrospective cohort study
Kayleen Ports, Jiahui Dai, Kyle Conniff, Maria M Corrada, Spero M Manson, Joan O’Connell, Luohua Jiang
The Lancet Regional Health Published:2025 Feb 13
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lana.2025.101013
Summary
Background
Dementia is an increasing concern among American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) communities, yet machine learning models utilizing electronic health record (EHR) data have not been developed or validated for this population. This study aimed to develop a two-year dementia risk prediction model for AI/AN individuals actively using Indian Health Service (IHS) and Tribal health services.
Methods
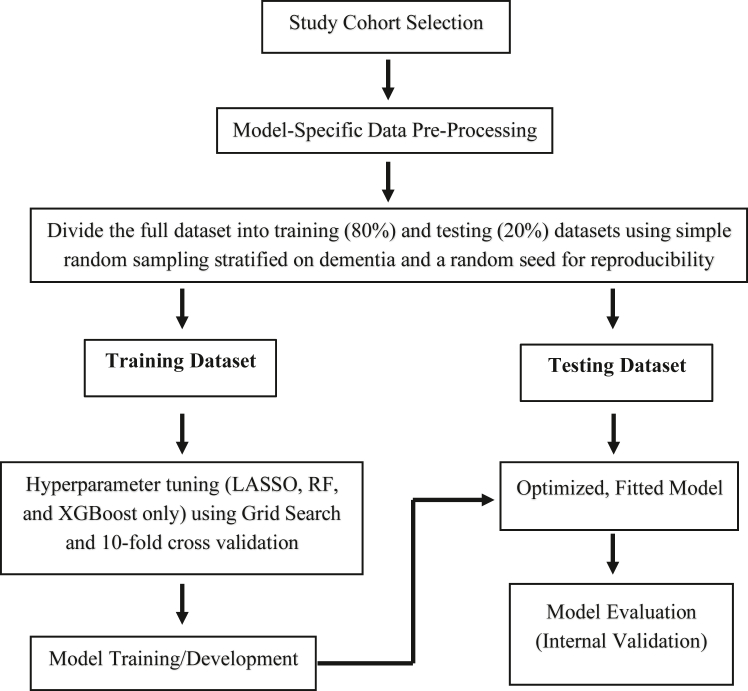
Seven years of data were obtained from the IHS National Data Warehouse and related EHR databases and divided into a five-year baseline period (FY2007–2011) and a two-year dementia prediction period (FY2012–2013). Four algorithms were assessed: logistic regression, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO), random forest, and eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). Dementia Risk Score (DRS)-based and extended models were developed for each algorithm, with performance evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
Findings
The study cohort included 17,398 AI/AN adults aged ≥ 65 years who were dementia-free at baseline, of whom 59.8% were female. Over the two-year follow-up, 611 individuals (3.5%) were diagnosed with incident dementia. Extended models for logistic regression, LASSO, and XGBoost performed comparably: AUCs (95% CI) of 0.83 (0.79, 0.86), 0.83 (0.79, 0.86), and 0.82 (0.79, 0.86). These top-performing models shared 12 of the 15 highest-ranked predictors, with novel predictors including service utilization.
Interpretation
Machine learning algorithms utilizing EHR data can effectively predict two-year dementia risk among AI/AN older adults. These models could aid IHS and Tribal health clinicians in identifying high-risk individuals, facilitating timely interventions and improved care coordination.
Funding
NIH.