2025-02-04 カリフォルニア大学サンフランシスコ校(UCSF)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ucsf.edu/news/2025/01/429411/how-hungry-fat-cells-could-someday-starve-cancer-death
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-024-02551-2
人工脂肪細胞の移植が癌モデルの腫瘍進行を抑制する Implantation of engineered adipocytes suppresses tumor progression in cancer models
Hai P. Nguyen,Kelly An,Yusuke Ito,Bhushan N. Kharbikar,Rory Sheng,Breanna Paredes,Elizabeth Murray,Kimberly Pham,Michael Bruck,Xujia Zhou,Cassandra Biellak,Aki Ushiki,Mai Nobuhara,Sarah L. Fong,Daniel A. Bernards,Filipa Lynce,Deborah A. Dillon,Mark Jesus M. Magbanua,Laura A. Huppert,Heinz Hammerlindl,Jace Anton Klein,Luis Valdiviez,Oliver Fiehn,Laura Esserman,… Nadav Ahituv
Nature Biotechnology Published:04 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02551-2
Abstract
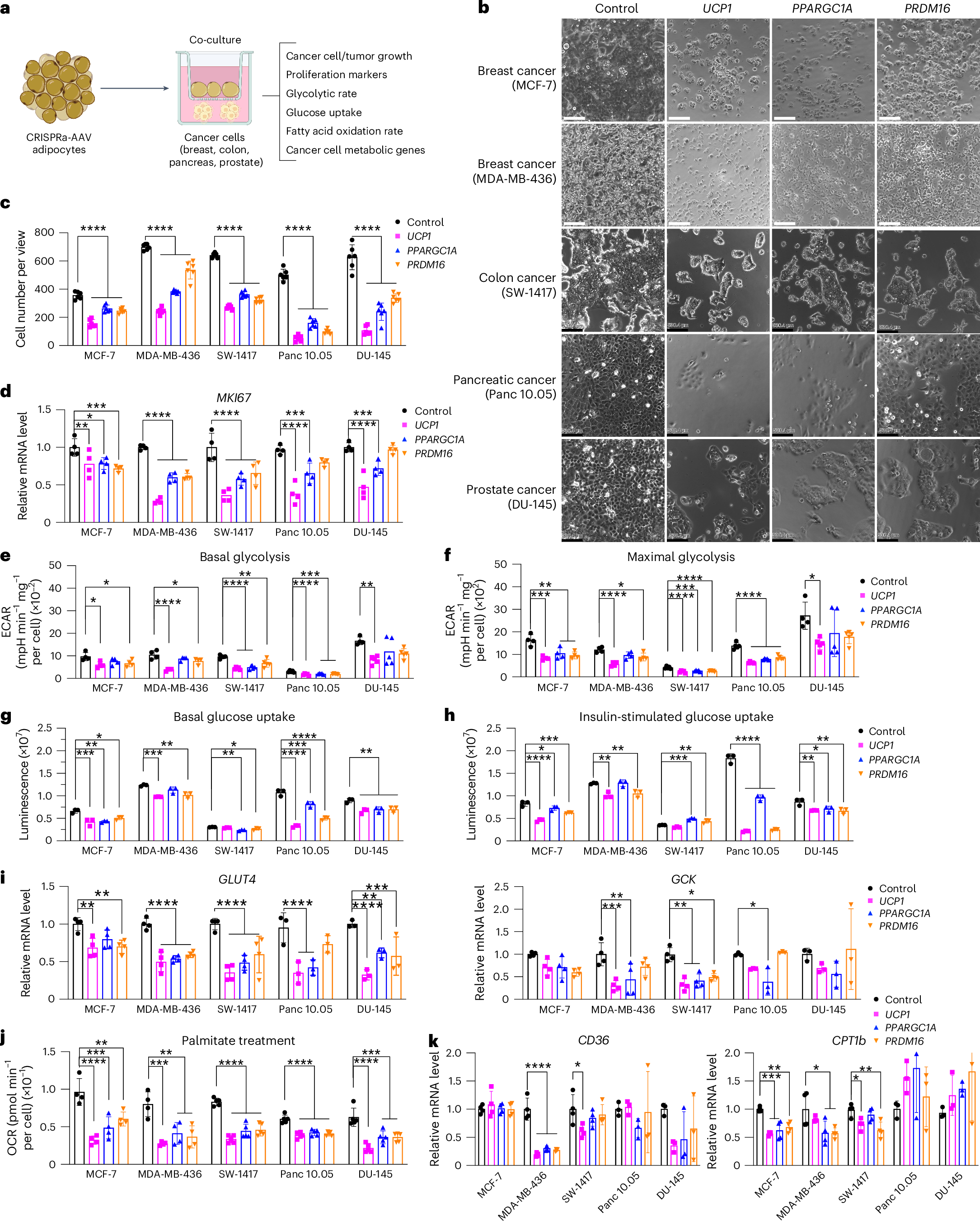
Tumors exhibit an increased ability to obtain and metabolize nutrients. Here, we implant engineered adipocytes that outcompete tumors for nutrients and show that they can substantially reduce cancer progression, a technology termed adipose manipulation transplantation (AMT). Adipocytes engineered to use increased amounts of glucose and fatty acids by upregulating UCP1 were placed alongside cancer cells or xenografts, leading to significant cancer suppression. Transplanting modulated adipose organoids in pancreatic or breast cancer genetic mouse models suppressed their growth and decreased angiogenesis and hypoxia. Co-culturing patient-derived engineered adipocytes with tumor organoids from dissected human breast cancers significantly suppressed cancer progression and proliferation. In addition, cancer growth was impaired by inducing engineered adipose organoids to outcompete tumors using tetracycline or placing them in an integrated cell-scaffold delivery platform and implanting them next to the tumor. Finally, we show that upregulating UPP1 in adipose organoids can outcompete a uridine-dependent pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma for uridine and suppress its growth, demonstrating the potential customization of AMT.