2025-04-16 北海道大学,東邦大学,札幌医科大学,旭川医科大学,大阪公立大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/04/post-1856.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250416_pr.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-58049-1
迅速かつ統合的な細菌進化解析による、肺炎桿菌の遺伝子変異と臨床リスクの解明 Rapid and Integrated Bacterial Evolution Analysis unveils gene mutations and clinical risk of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Kojiro Uemura,Toyotaka Sato,Soh Yamamoto,Noriko Ogasawara,Jirachaya Toyting,Kotaro Aoki,Akira Takasawa,Masayuki Koyama,Atsushi Saito,Takayuki Wada,Kaho Okada,Yurie Yoshida,Koji Kuronuma,Chie Nakajima,Yasuhiko Suzuki,Motohiro Horiuchi,Kenichi Takano,Satoshi Takahashi,Hirofumi Chiba & Shin-ichi Yokota
Nature Communications Published:25 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58049-1
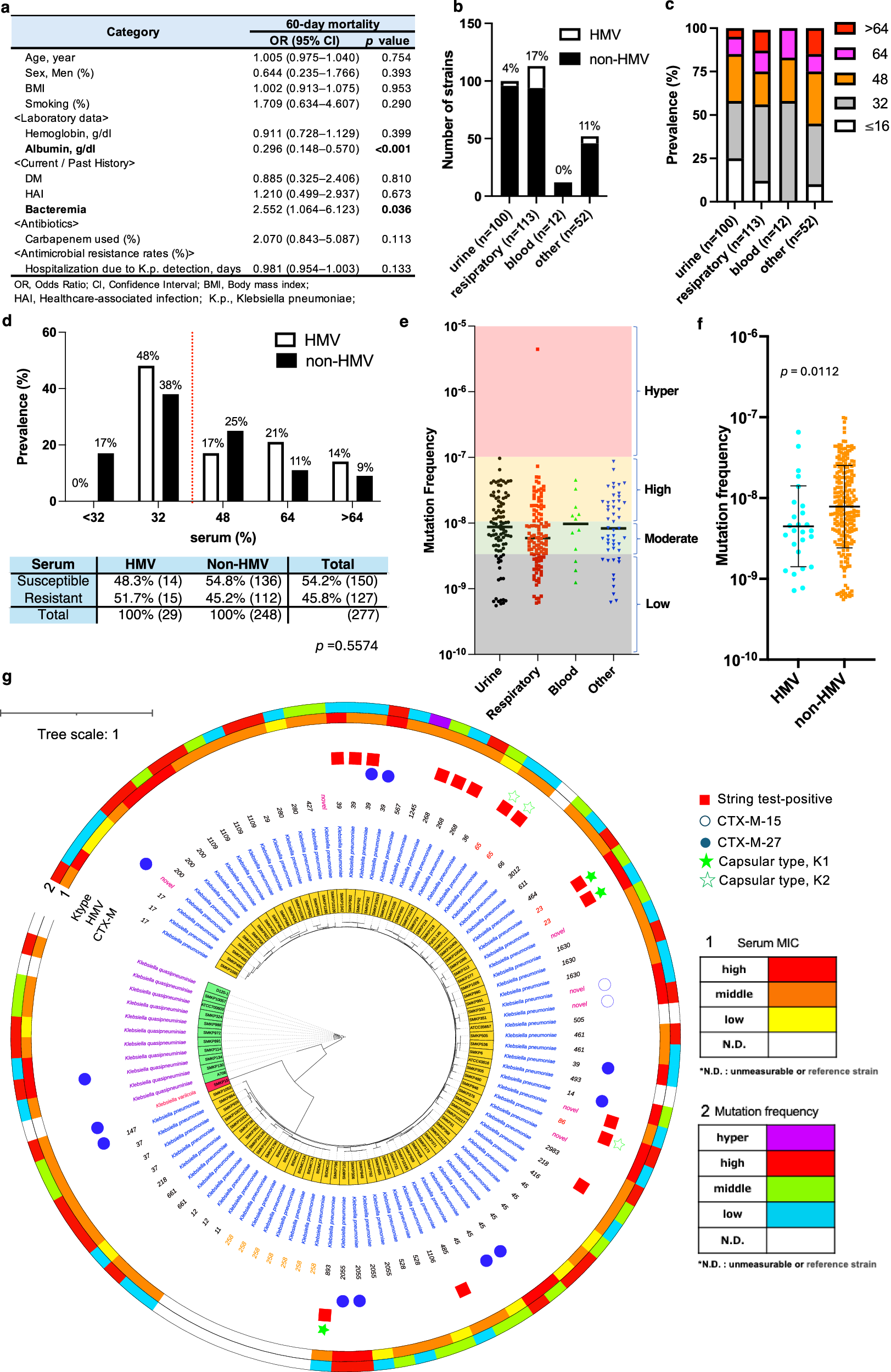
Abstract
Bacteria continually evolve. Previous studies have evaluated bacterial evolution in retrospect, but this approach is based on only speculation. Cohort studies are reliable but require a long duration. Additionally, identifying which genetic mutations that have emerged during bacterial evolution possess functions of interest to researchers is an exceptionally challenging task. Here, we establish a Rapid and Integrated Bacterial Evolution Analysis (RIBEA) based on serial passaging experiments using hypermutable strains, whole-genome and transposon-directed sequencing, and in vivo evaluations to monitor bacterial evolution in a cohort for one month. RIBEA reveals bacterial factors contributing to serum and antimicrobial resistance by identifying gene mutations that occurred during evolution in the major respiratory pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae. RIBEA also enables the evaluation of the risk for the progression and the development of invasive ability from the lung to blood and antimicrobial resistance. Our results demonstrate that RIBEA enables the observation of bacterial evolution and the prediction and identification of clinically relevant high-risk bacterial strains, clarifying the associated pathogenicity and the development of antimicrobial resistance at genetic mutation level.