2025-05-07 東京科学大学
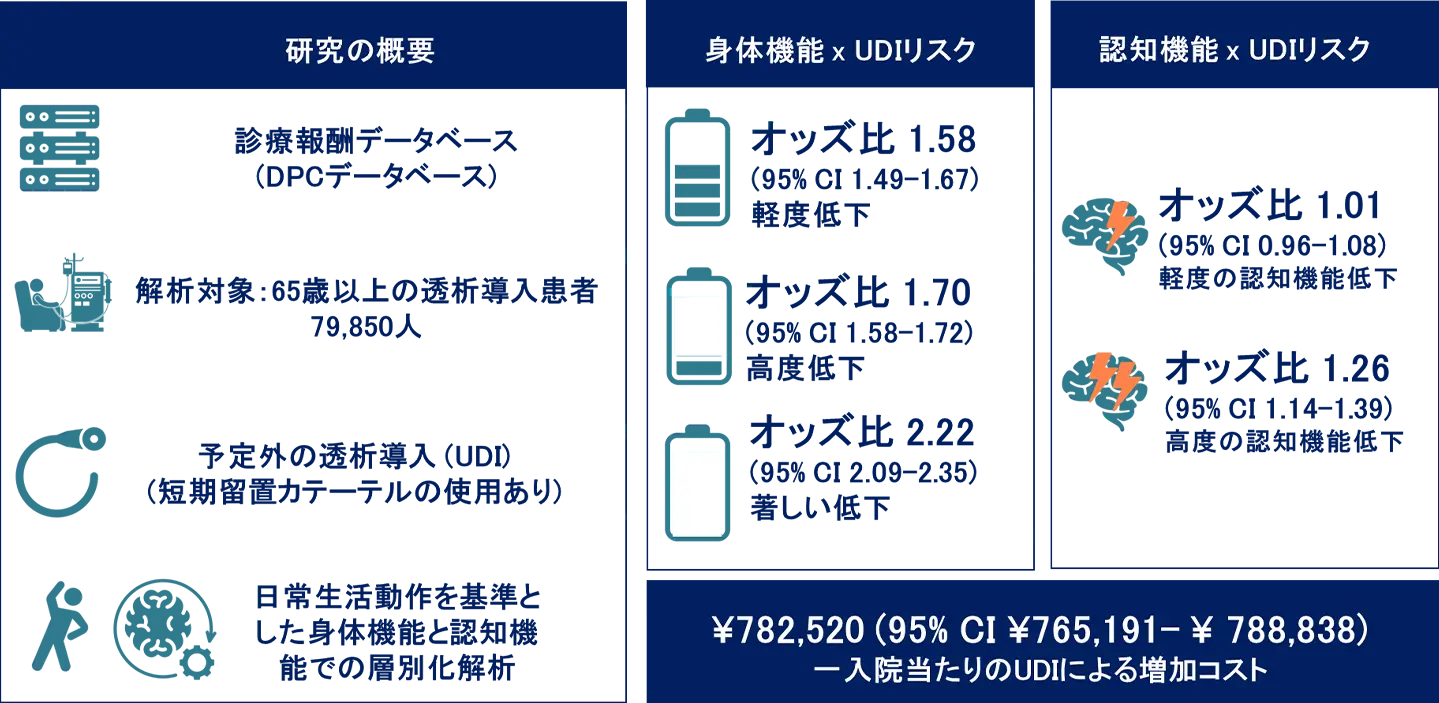
図1. 研究概要:身体機能障害・認知機能低下とUDIリスクの関連
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/noay07ff2n45
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1459&prevId=&key=5ac7e923c1fb8e459df201aa43b6714d.pdf
- https://www.kireports.org/article/S2468-0249(25)00238-4/fulltext
予定外の透析開始に伴う認知機能障害と身体機能障害 Cognitive Impairment and Physical Dysfunction Associated With Unplanned Dialysis Initiation
Yuta Nakano ∙ Shintaro Mandai smandai.kid@tmd.ac.jp ∙ Yutaro Mori ∙ … ∙ Eisei Sohara ∙ Kiyohide Fushimi ∙ Shinichi Uchida
Kidney International Reports Published:April 17, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2025.04.018
Abstract
Introduction
Unplanned dialysis initiation (UDI) is associated with poor outcomes and high medical costs. Although aging is a prominent risk factor for UDI, the roles of age-related factors such as cognitive impairment and physical dysfunction remain underexplored. This study aimed to clarify the associations of cognitive impairment and physical dysfunction with UDI and additional medical costs.
Methods
This study used a Japanese administrative claims database to analyze 79,850 patients aged ≥ 65 years (median age: 76 ys; 31.6% females) who began receiving dialysis. UDI was defined as starting dialysis with a temporary catheter. Physical function and cognitive impairment were classified based on mobility and daily living abilities. We assessed the association using logistic regression. Additional medical costs were estimated via generalized linear regression.
Results
UDI occurred in 16,176 patients (20%). Compared with the normal group, the odds ratios (ORs) for UDI were 1.58 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.49–1.67) for low physical function, 1.70 (95% CI: 1.58–1.82) for very low, and 2.22 (95% CI: 2.09–2.35) for extremely low physical function. For cognitive impairment, the ORs were 1.02 (95% CI: 0.96–1.08) for mild impairment and 1.26 (95% CI: 1.14–1.39) for severe impairment relative to normal. The average marginal cost of UDI was $7178 [95% CI: $7019–$7338] per admission. A combination of physical dysfunction and cognitive impairment further increased UDI risk and inpatient care costs.
Conclusion
Older adults with cognitive impairment and physical dysfunction face a higher risk of UDI. Early intervention for these patients may reduce UDI and its associated costs.