2025-05-07 東京大学
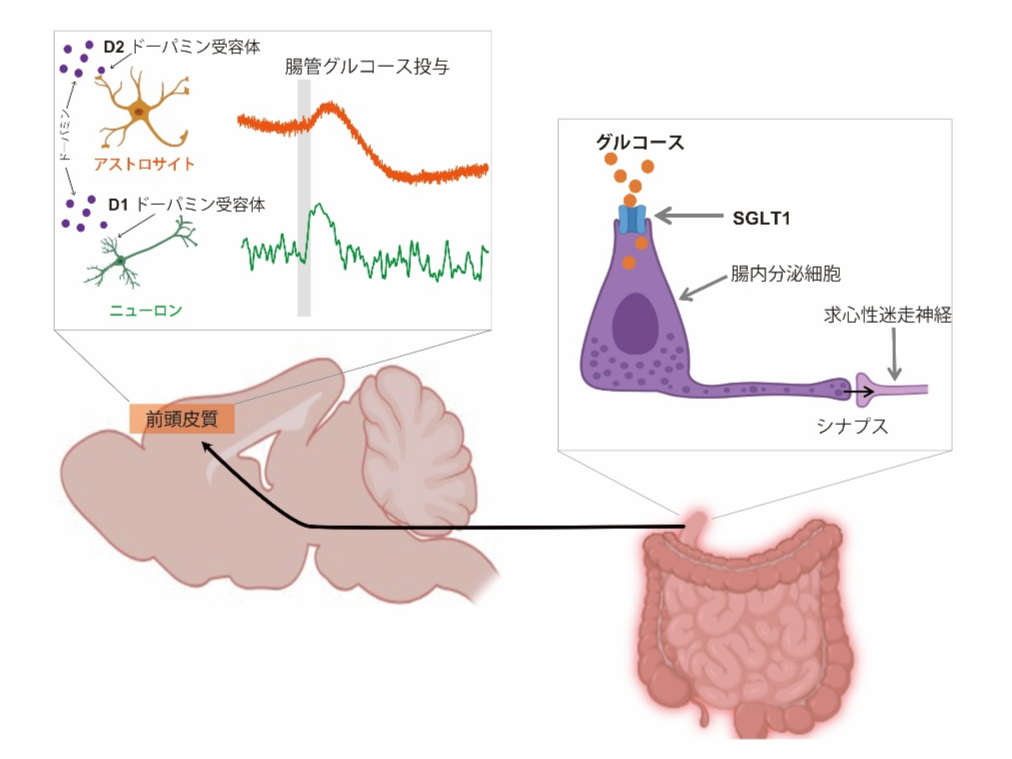 本研究で明らかになった腸脳相関による糖嗜好性調節機構の一端
本研究で明らかになった腸脳相関による糖嗜好性調節機構の一端
<関連情報>
- https://www.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp/info/news/topics/20250507140000.html
- https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(25)00700-X
腸-脳神経連絡における迷走神経を介して伝達される即時グルコースシグナル Immediate glucose signaling transmitted via the vagus nerve in gut–brain neural communication
Serika Yamada ∙ Akiyo Natsubori ∙ Kazuki Harada ∙ Takashi Tsuboi ∙ Hiromu Monai
iScience Published:May 5, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2025.112439
Highlights
- Gut glucose sensing via SGLT1 rapidly activates frontal cortex astrocytes and neurons
- Cortical astrocyte activation after gut glucose sensing robustly occurs also by D2DR
- Cortical neurons activation after gut glucose sensing robustly occurs so also by D1DR
- Frontal cortex activation after gut glucose sensing is absent in mice under CMRS
Summary
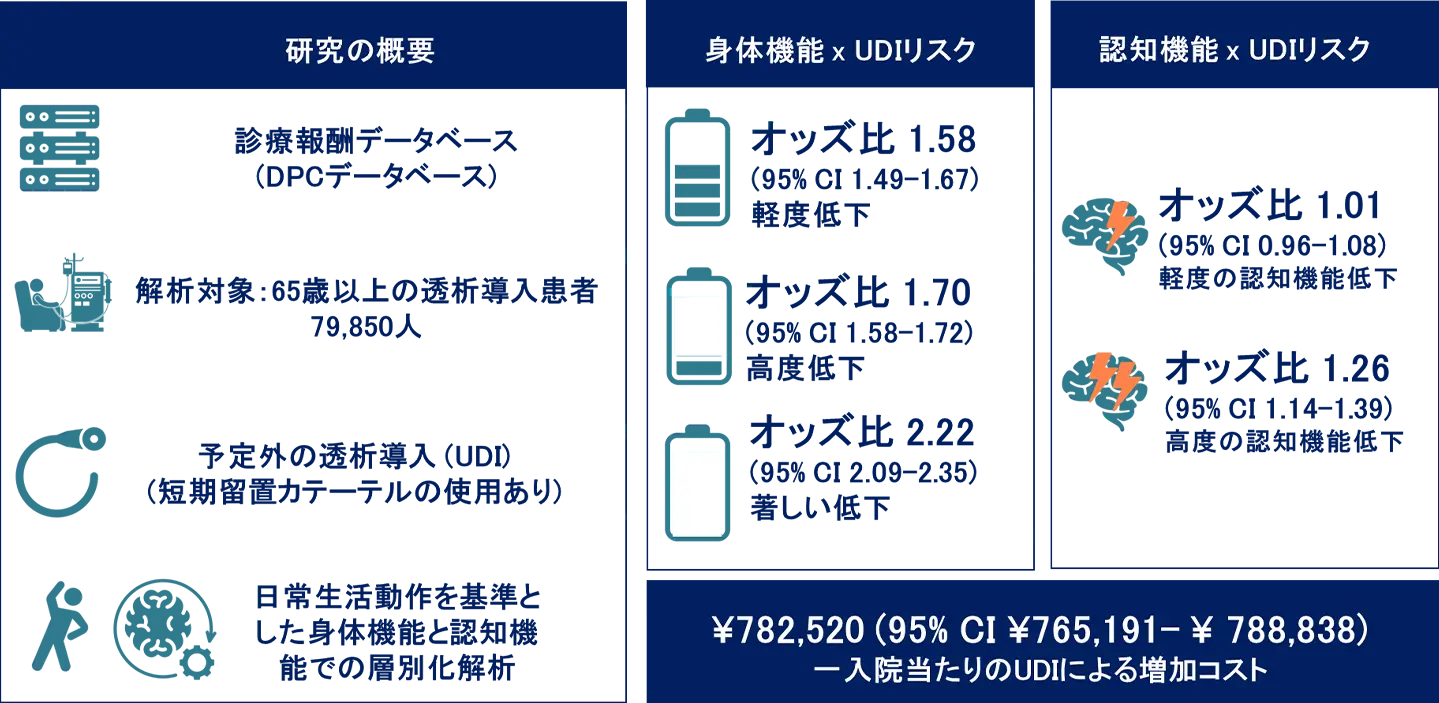
Sucrose consumption is influenced by certain gut–brain signaling mechanisms. One possible pathway could be the interaction between the vagus nerve and the central nervous system, mediated by neuropod cells forming synaptic connections with vagus nerves, which immediately activate the central dopaminergic pathways. In this study, we demonstrated that intestinal glucose administration activates the frontal cortex via the vagus nerve and central dopamine signaling. The immediate activation of both the vagus nerve and the frontal cortex was mediated by the sodium–glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). Furthermore, Ca2+ signal activation in both astrocytes and neurons in the frontal cortex was mediated by D2 and D1 receptors, respectively. Finally, we showed that psychological stress, which causes a sucrose preference reduction, significantly diminished the activation levels of both the vagus nerve and the frontal cortex. These findings highlight the role of a comprehensive gut–brain network via vagus nerves in modulating sucrose preference.