2025-05-20 福井県立大学,理化学研究所
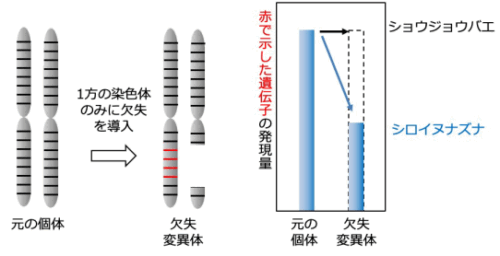
図2.一方の染色体の一部を欠失させた変異体の遺伝子発現量の変化の模式図 重イオンビームで 1 本の染色体だけに欠失を引き起こすと、通常2つずつある遺伝子が1つずつになる(左図、赤線)。これらの遺伝子の発現量を調査したところおよそ半分に減少することがわかった(右図)。
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2025/20250520_3/index.html
- https://www.riken.jp/medialibrary/press/2025/20250520_3.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-98141-6
シロイヌナズナにおけるヘテロ接合体欠失が表現型の変化と用量補償に及ぼす影響 Effect of heterozygous deletions on phenotypic changes and dosage compensation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Takuya Ikoma,Ryo Nishijima,Miho Ikeda,Kotaro Ishii,Asanga Deshappriya Nagalla,Tomoko Abe & Yusuke Kazama
Scientific Reports Published:13 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98141-6
Abstract
Heterozygous deletions, which include a large number of genes, are often caused by the induction of mutations. The induction of gene dosage compensation should be considered when assessing the effects of heterozygous deletions on phenotypic changes. This mechanism is known to balance the expression levels of genes with different copy numbers in sex chromosomes, but it is also known to operate in autosomes. In the present study, 12 Arabidopsis thaliana BC1 mutants with heterozygous deletions were produced by crossing wild-type Col-0 plants with mutants induced by heavy ion beams. The sizes of the deletions ranged from 50.9 kb to 2.03 Mb, and the number of deleted genes ranged from 8 to 92. Nine of the 12 BC1 mutants showed phenotypic changes in fresh weight 14 days after cultivation or during the flowering period. RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analyses of 14-day-old leaves, 40-day-old leaves, and flower buds showed that dosage compensation did not occur in any stage or tissue tested. These results indicate that heterozygous deletions cause phenotypic changes owing to the absence of dosage compensation.

