2025-05-27 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
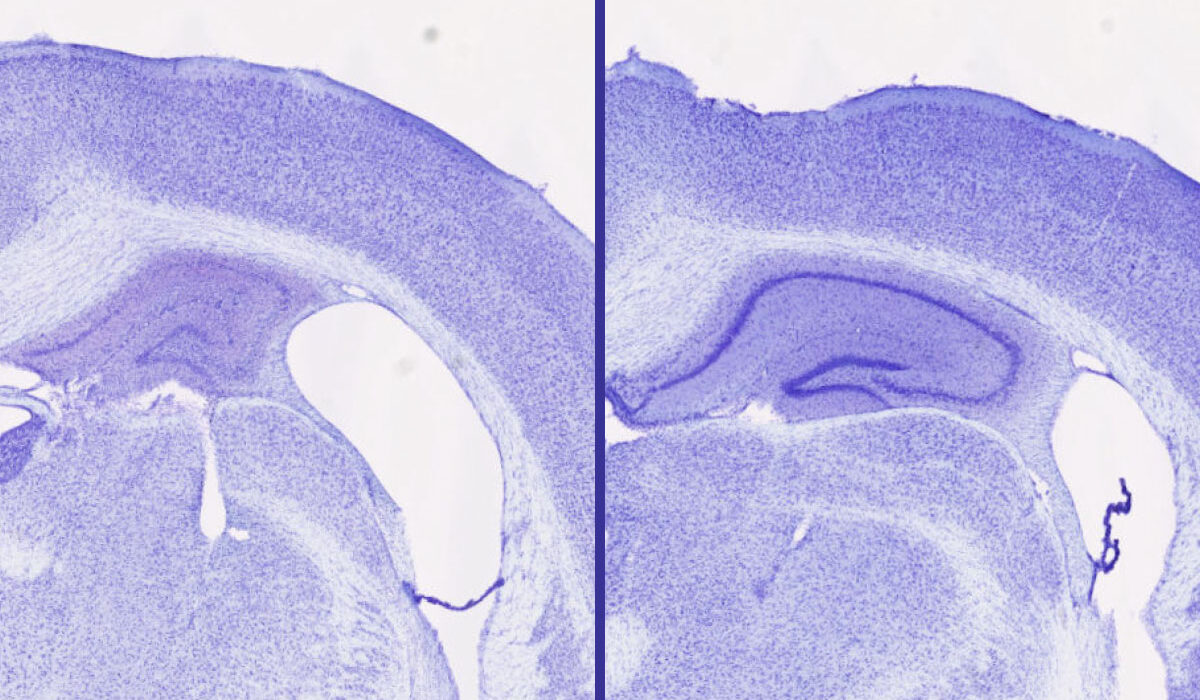 Shown are cross-sections of brain tissue from two mice genetically prone to tau accumulation. Treatment with lemborexant (right) results in larger volume in the hippocampus (central purple spiral), important for memory, and a smaller gap in brain tissue (white space) compared with no treatment (left). (Image: Samira Parhizkar/WashU Medicine)
Shown are cross-sections of brain tissue from two mice genetically prone to tau accumulation. Treatment with lemborexant (right) results in larger volume in the hippocampus (central purple spiral), important for memory, and a smaller gap in brain tissue (white space) compared with no treatment (left). (Image: Samira Parhizkar/WashU Medicine)
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2025/05/sleep-aid-blocks-neurodegeneration-in-mice/
- https://medicine.washu.edu/news/sleep-aid-blocks-neurodegeneration-in-mice/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-01966-7
レンボレキサントはタウオパチーモデルマウスにおいてタウが介在する睡眠障害とオスの神経変性を改善する Lemborexant ameliorates tau-mediated sleep loss and neurodegeneration in males in a mouse model of tauopathy
Samira Parhizkar,Xin Bao,Wei Chen,Nicholas Rensing,Yun Chen,Michal Kipnis,Sihui Song,Grace Gent,Eric Tycksen,Melissa Manis,Choonghee Lee,Javier Remolina Serrano,Megan E. Bosch,Emily Franke,Carla M. Yuede,Eric C. Landsness,Michael Wong & David M. Holtzman
Nature Neuroscience Published:27 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-01966-7
Abstract
Sleep disturbances are associated with the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and primary tauopathies. Here we demonstrate that administration of the dual orexin receptor antagonist lemborexant in the P301S/E4 mouse model of tauopathy improves tau-associated impairments in sleep–wake behavior. It also protects against chronic reactive microgliosis and brain atrophy in male P301S/E4 mice by preventing abnormal phosphorylation of tau. These neuroprotective effects in males were not observed after administration of the nonorexinergic drug zolpidem that similarly promoted nonrapid eye movement sleep. Furthermore, both genetic ablation of orexin receptor 2 and lemborexant treatment reduced wakefulness and decreased seeding and spreading of phosphorylated tau in the brain of wild-type mice. These findings raise the therapeutic potential of targeting sleep by orexin receptor antagonism to prevent abnormal tau phosphorylation and limit tau-induced damage.