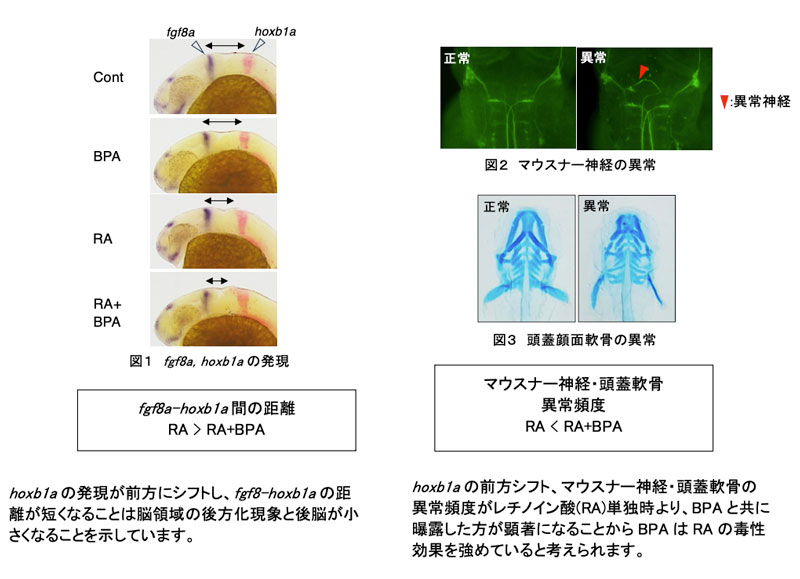
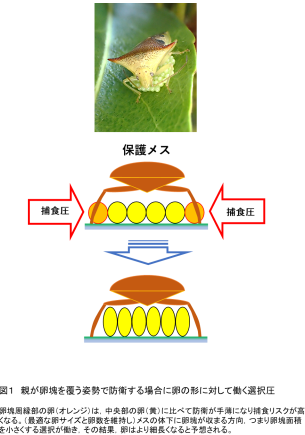
2025-05-29 京都大学

<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-05-29-3
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-05/web_2505_Arai-53113fb0fc17739ff3d413ed60150213.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jha2.70061
急性白血病に対する全身照射に基づく強化骨髄移植レジメンの有効性-国際共同研究 Efficacy of Total-Body Irradiation-based Intensified Myeloablative Regimens for Acute Leukemia—An International Collaborative Study
Yasuyuki Arai, Ruta Brazauskas, Naya He, A. Samer Al-Homsi, Saurabh Chhabra, Minoo Battiwalla, Masamitsu Yanada, Amir Steinberg, Miguel Angel Diaz Perez, Sanghee Hong …
eJHaem Published: 28 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/jha2.70061
ABSTRACT
Background
In this study, we compared outcomes of intensified myeloablative conditioning regimens using large registry data from Japan (Japanese Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy) and the United States (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research).
Methods
Adult patients who underwent their first myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acute leukemia in remission between 2010 and 2018 using conditioning regimens of cyclophosphamide plus total-body irradiation (CY/TBI), CY/TBI+cytarabine (AraC), or CY/TBI+etoposide (VP16) were included.
Results
The acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cohort (N = 480, 38.8%) indicated that overall survival (OS) was poorer in CY/TBI+AraC (hazard ratio [HR] 1.46, p < 0.001) and CY/TBI+VP16 (HR 1.39, p = 0.059) compared to CY/TBI. Relapse was not suppressed, while treatment-related mortality (TRM) was significantly higher (HR 1.78 and 1.74, p < 0.001 and 0.018, respectively). In the acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cohort (N = 3901, 61.2%), OS was comparable among these regimens. With intensified regimens, relapse was significantly suppressed in CY/TBI+VP16 (HR 0.74, p = 0.005), while TRM was higher (HR 1.21, p = 0.077). No interactions were observed regarding the country.
Conclusion
In AML adding AraC and VP16 to CY/TBI had an adverse effect on OS. Conversely, in ALL, adding VP16 or AraC to CY/TBI did not affect survival, but the addition of VP16 reduced the risk of relapse.
Clinical Trial Registration
The authors have confirmed clinical trial registration is not needed for this submission.