2025-06-06 ジョンズ・ホプキンス大学 (JHU)
<関連情報>
- https://hub.jhu.edu/2025/06/06/artificial-intelligence-infectious-disease-forecasting/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-025-00798-6
大規模言語モデルを用いたリアルタイム感染症予測の進展 Advancing real-time infectious disease forecasting using large language models
Hongru Du,Yang Zhao,Jianan Zhao,Shaochong Xu,Xihong Lin,Yiran Chen,Lauren M. Gardner & Hao ‘Frank’ Yang
Nature Computational Science Published:06 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-025-00798-6
Abstract
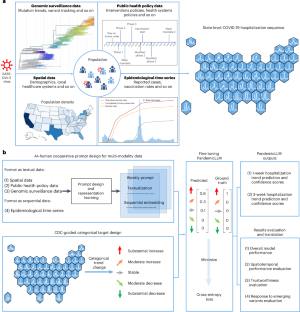
Forecasting the short-term spread of an ongoing disease outbreak poses a challenge owing to the complexity of contributing factors, some of which can be characterized through interlinked, multi-modality variables, and the intersection of public policy and human behavior. Here we introduce PandemicLLM, a framework with multi-modal large language models (LLMs) that reformulates real-time forecasting of disease spread as a text-reasoning problem, with the ability to incorporate real-time, complex, non-numerical information. This approach, through an artificial intelligence–human cooperative prompt design and time-series representation learning, encodes multi-modal data for LLMs. The model is applied to the COVID-19 pandemic, and trained to utilize textual public health policies, genomic surveillance, spatial and epidemiological time-series data, and is tested across all 50 states of the United States for a duration of 19 months. PandemicLLM opens avenues for incorporating various pandemic-related data in heterogeneous formats and shows performance benefits over existing models.