20025-06-17 千葉大学
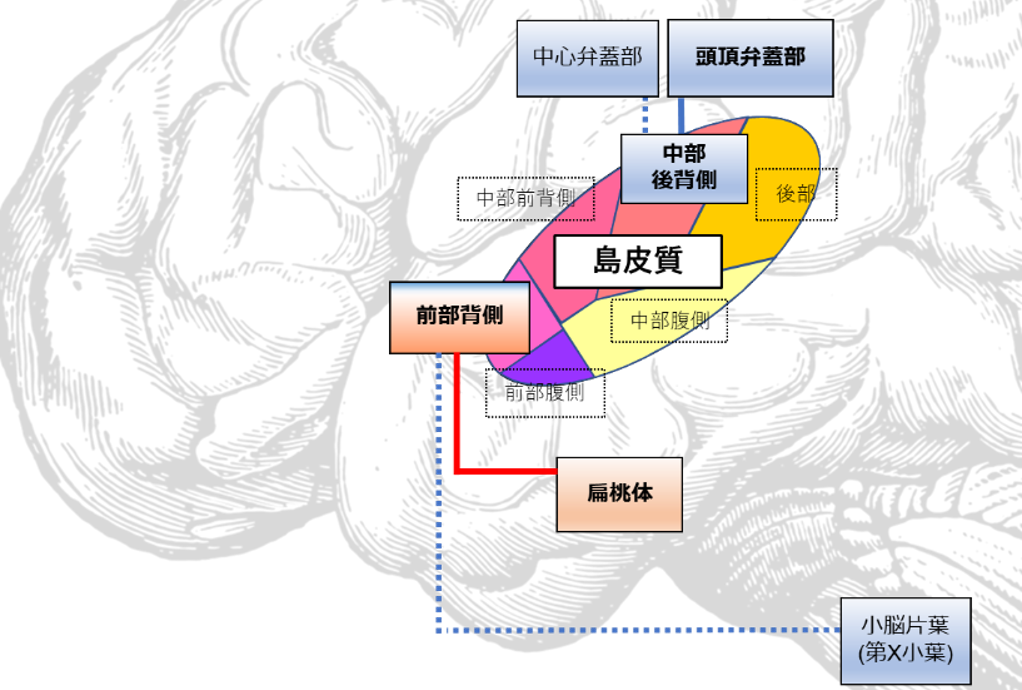 神経性やせ症で生じていた機能的結合性の変化
神経性やせ症で生じていた機能的結合性の変化
(模式図 赤線:機能亢進 青線:機能低下 実線:統計的信頼性が高い)
<関連情報>
- https://www.chiba-u.ac.jp/news/research-collab/post_551.html
- https://www.chiba-u.ac.jp/news/files/pdf/250617_SR.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-03641-0
神経性食欲不振症における島皮質の安静時機能的結合の変化を解明するための多施設横断研究(機能局在別に細分化 A multicenter cross-sectional study to elucidate altered resting-state functional connectivity of the insular cortex in anorexia nervosa, segmented by functional localization
Yusuke Sudo,Rio Kamashita,Tsunehiko Takamura,Sayo Hamatani,Noriko Numata,Koji Matsumoto,Yasuhiro Sato,Yumi Hamamoto,Tomotaka Shoji,Tomohiko Muratsubaki,Motoaki Sugiura,Shin Fukudo,Michiko Kawabata,Momo Sunada,Tomomi Noda,Keima Tose,Masanori Isobe,Naoki Kodama,Shingo Kakeda,Masatoshi Takahashi,Hiroaki Adachi,Shu Takakura,Motoharu Gondo,Kazufumi Yoshihara,… Yoshiyuki Hirano
Scientific Reports Published:31 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-03641-0
Abstract
Although changes in insular function have been thought to play a central role in the pathophysiology of anorexia nervosa (AN), due to factors such as insufficient sample size, there have been no studies examining changes in resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) between insula and whole brain in AN, based on functional localization of insula. Here, we subdivided insula into 6 regions per side based on functional localization and reanalyzed previously published functional magnetic resonance imaging data from 114 female patients with AN and 135 female healthy controls (HC). We calculated the rsFCs between ROIs and compared the results between groups, with the 12 insular regions serving as seed ROIs and 142 regions of the whole brain as target ROIs. Compared to HC, AN patients had a increased rsFC between dorsal anterior insula (daIC) and amygdala, and a decreased rsFC between posterior division of dorsal middle insula (pdmIC) and opercular cortex (false discovery rate [FDR] corrected p-value < 0.05 with analysis-level correction, which means that FDR correction was applied to all seed ROIs and all target ROI combinations). These rsFC changes may be the neurological basis for AN symptoms, such as hypersensitivity to negative stimuli, taste disorder, and enhanced taste aversion learning.