2025-07-25 東京科学大学
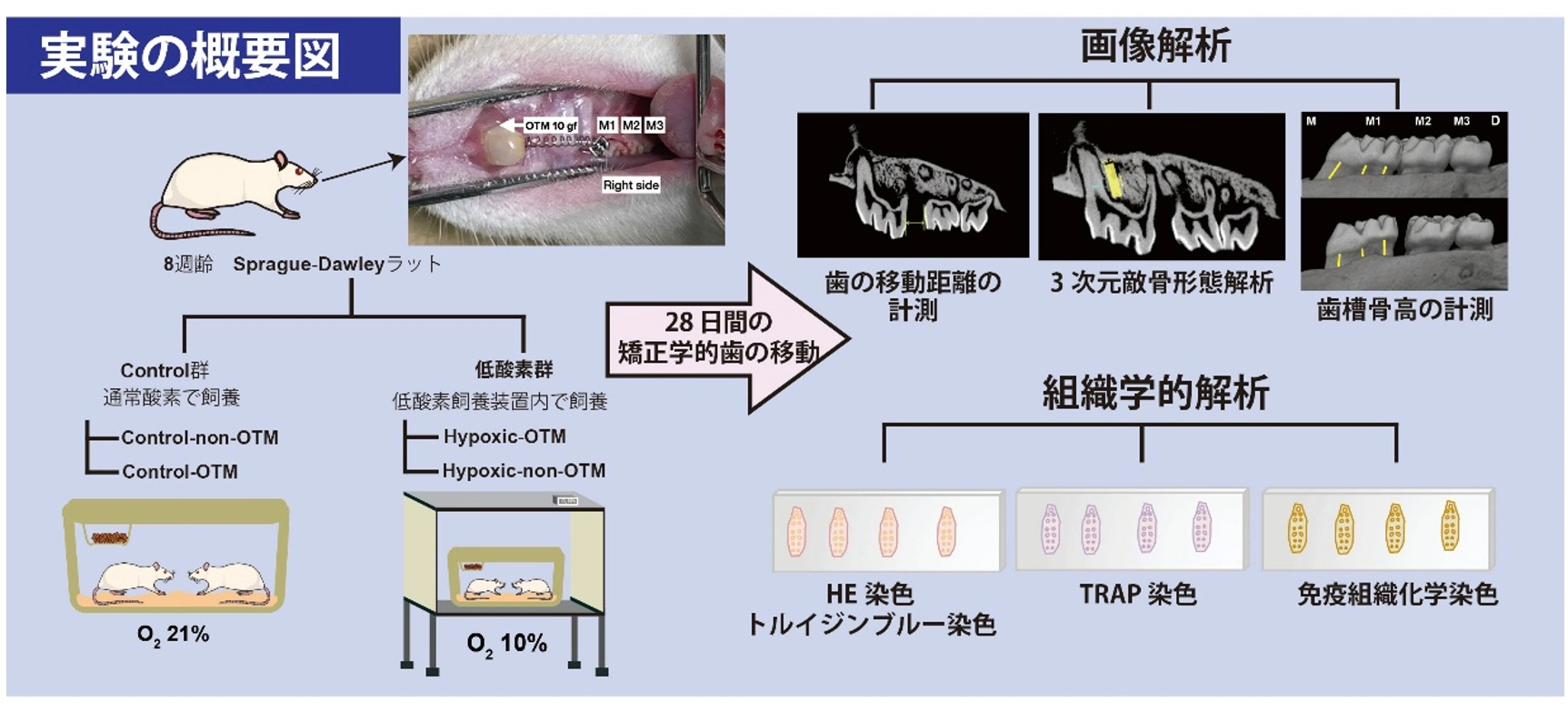
図1.実験の概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/3nh1xgkz0796
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2010&prevId=&key=634349b547773393d0c31ab38f9c878b.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-07949-9
ラットにおける全身性かつ持続的な低酸素状態が歯列矯正の歯の移動に与える影響 The effects of systemic and sustained hypoxia on orthodontic tooth movement in rats
Kwanrat Ploysongsang,Yukiho Kobayashi,Yeming Lu,Yuki Niki,Janeta Chavanavesh & Keiji Moriyama
Scientific Reports Published:01 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-07949-9
Abstract
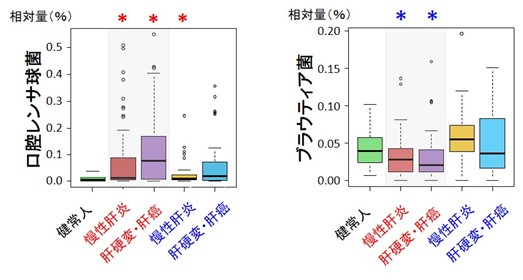
During orthodontic tooth movement (OTM), local hypoxia on the compression side stimulates cellular remodelling of periodontal tissues. We investigated the effects of systemic, sustained hypoxia on OTM in vivo. OTM was performed on the right maxillary first molar (M1) of 8-week-old male Sprague–Dawley rats using a 10-gf nickel-titanium closed-coil spring for 4 weeks under control (21% O2, n = 9) or hypoxic (10% O2, n = 9) conditions. Micro-computed tomography was used to measure OTM distances, alveolar bone morphometric parameters, and M1 buccal alveolar bone levels. Osteoclast differentiation and periodontal ligament (PDL) cell proliferation were determined using tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in M1 periodontal tissues were analysed using immunofluorescence. The hypoxia-OTM group showed significantly accelerated tooth movement, significantly decreased M1 buccal alveolar bone levels, significantly greater numbers of TRAP-positive cells on the compression side, and significantly reduced Ki67-positive ratios in PDL tissues. The VEGF and RUNX2 fluorescence intensities on the tension side were higher in the control-OTM than in the hypoxia-OTM group. Our results demonstrate that systemic, sustained hypoxia affects OTM by altering osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation in vivo, resulting in reduced alveolar bone levels after OTM.