2025-08-19 イェール大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.yale.edu/2025/08/19/timing-everything-finding-treatment-windows-genetic-brain-disease
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-61921-9
chronODEフレームワーク:普通微分方程式と機械学習を用いたマルチオミクス時系列のモデリング The chronODE framework for modelling multi-omic time series with ordinary differential equations and machine learning
Beatrice Borsari,Mor Frank,Eve S. Wattenberg,Ke Xu,Susanna X. Liu,Xuezhu Yu & Mark Gerstein
Nature Communications Published:19 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-61921-9
Abstract
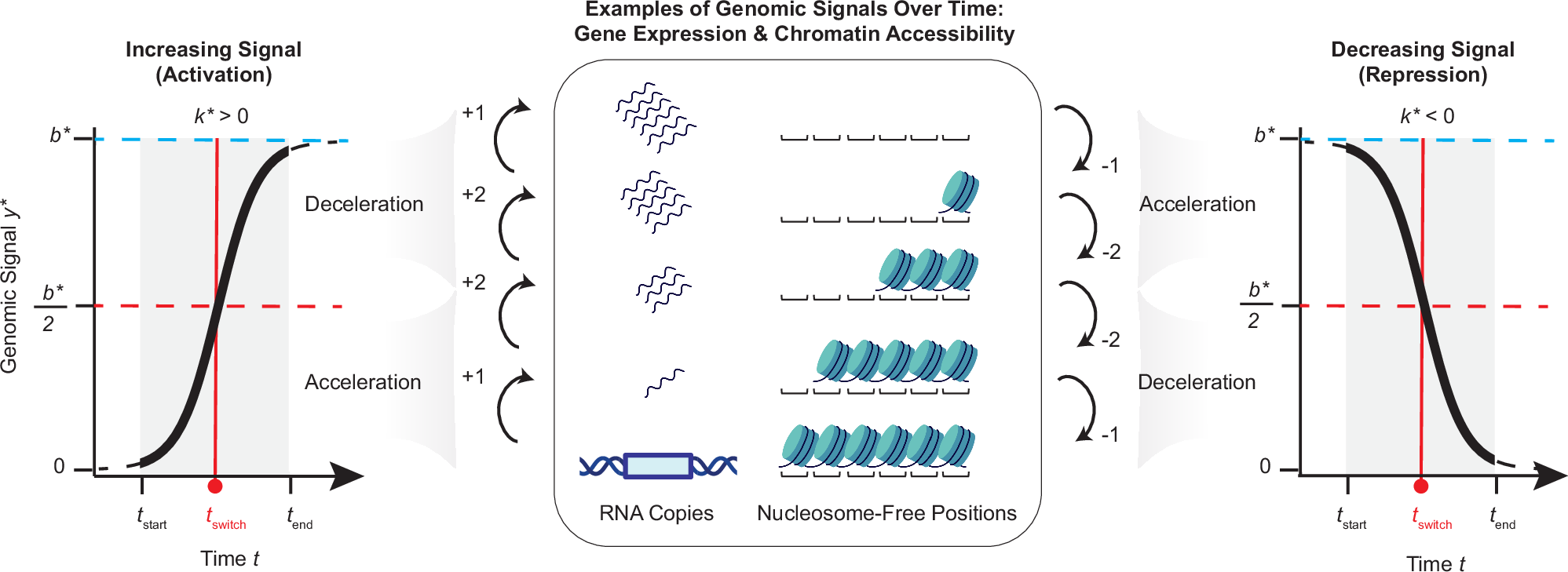
Many genome-wide studies capture isolated moments in cell differentiation or organismal development. Conversely, longitudinal studies provide a more direct way to study these kinetic processes. Here, we present an approach for modeling gene-expression and chromatin kinetics from such studies: chronODE, an interpretable framework based on ordinary differential equations. chronODE incorporates two parameters that capture biophysical constraints governing the initial cooperativity and later saturation in gene expression. These parameters group genes into three major kinetic patterns: accelerators, switchers, and decelerators. Applying chronODE to bulk and single-cell time-series data from mouse brain development reveals that most genes (~87%) follow simple logistic kinetics. Among them, genes with rapid acceleration and high saturation values are rare, highlighting biochemical limitations that prevent cells from attaining both simultaneously. Early- and late-emerging cell types display distinct kinetic patterns, with essential genes ramping up faster. Extending chronODE to chromatin, we find that genes regulated by both enhancer and silencer cis-regulatory elements are enriched in brain-specific functions. Finally, we develop a bidirectional recurrent neural network to predict changes in gene expression from corresponding chromatin changes, successfully capturing the cumulative effect of multiple regulatory elements. Overall, our framework allows investigation of the kinetics of gene regulation in diverse biological systems.