2025-08-22 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
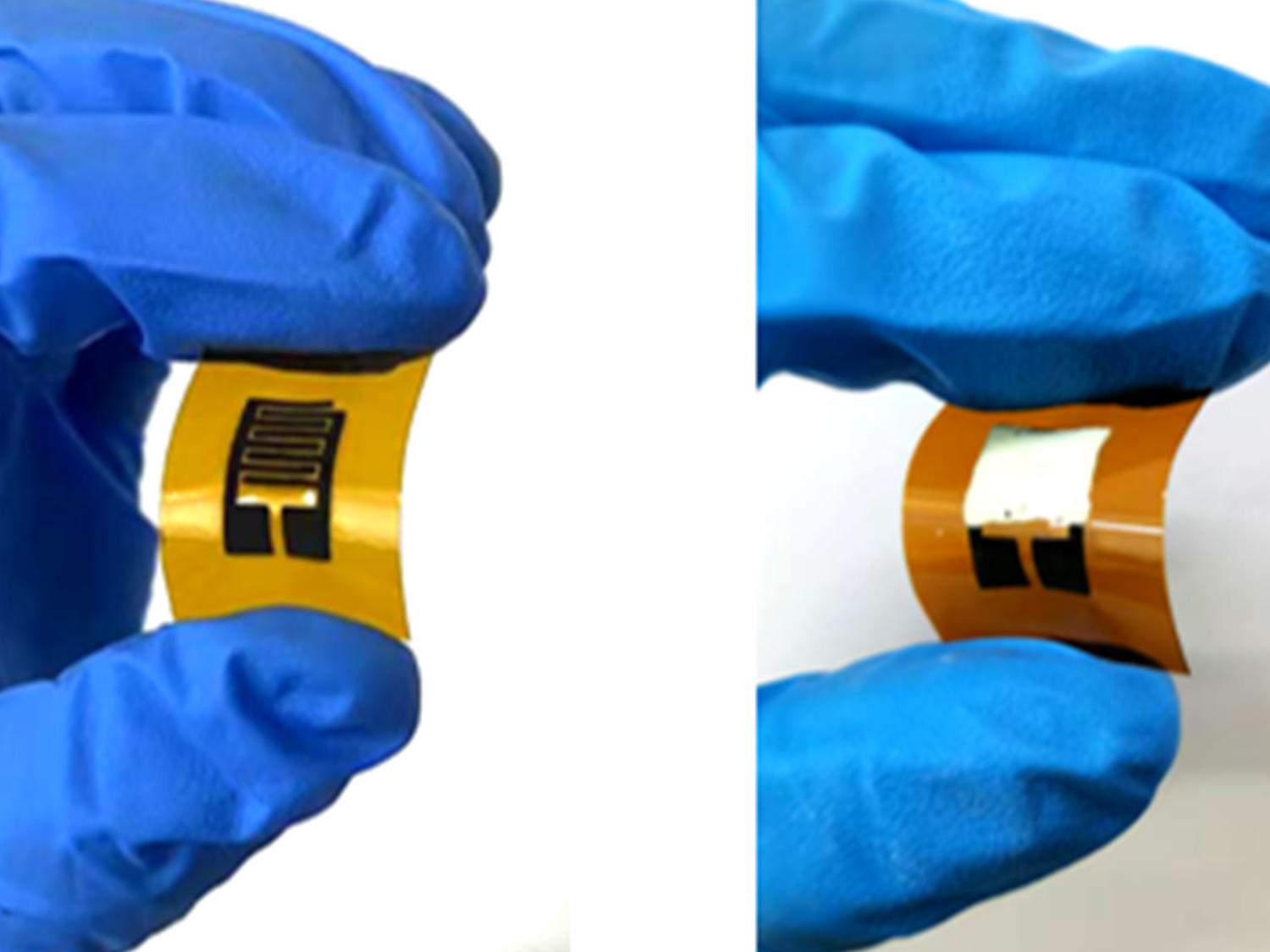
A team led by a researcher at Penn State has developed a sensor that can help diagnose diabetes and prediabetes on-site in a few minutes using just a breath sample. Credit: Provided by Larry Cheng . All Rights Reserved.
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/engineering/story/new-sensor-breath-fresh-air-diagnosing-diabetes
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1385894725056931?via%3Dihub
ZnO/LIGナノコンポジットを用いた室温でのアセトンガス検出:高感度かつ低検出限界を実現 ZnO/LIG nanocomposites to detect acetone gas at room temperature with high sensitivity and low detection limit
Li Yang, Wenyuan Fu, Ya Wang, Zhida Wang, Longbiao Mao, Luxiang Xu, Chengpeng Yao, Hongyu Zhang, Sisi Chen, Hui Zhang, Huanyu Cheng
Chemical Engineering Journal Available online: 13 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.164857
Highlights
- A highly sensitive ZnO/LIG-based acetone gas sensor with ultralow detection limit.
- The sensor exhibits large response, fast response/recovery time at room temperature.
- The resulting sensor can accurately detect acetone in highly humid environments.
- The sensor can differentiate diabetic patients from healthy individuals for early diagnostics.
Abstract
While the low-cost noninvasive measurements of diabetes based on exhalation diagnosis is of high interest, it is still difficult for the needed gas sensors to achieve high sensitivity, low detection limit, and low power consumption. This study presents a highly sensitive acetone gas sensor with ultralow detection limit based on zinc oxide (ZnO)/laser-induced graphene (LIG) composite with heterostructures on interdigitated electrodes prepared by one-step laser direct writing and simple drop casting. The resulting ZnO/LIG-based acetone gas sensor exhibits a large response of -24 % to 1 ppm acetone, a fast response recovery time of 21/23 s, and an ultralow experimentally demonstrated (or theoretical) detection limit of 4 ppb (or 334 ppt). Further combined with a molecular sieve coating layer, the acetone gas sensor can accurately detect acetone in the highly humid environments such as the exhaled breath and differentiate diabetic patients from healthy individuals for early diagnostics and treatment evaluations.