2025-10-16 カリフォルニア大学ロサンゼルス校(UCLA)
<関連情報>
- https://newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/blood-test-promise-in-early-als-detection-ucla
- https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-025-01542-5
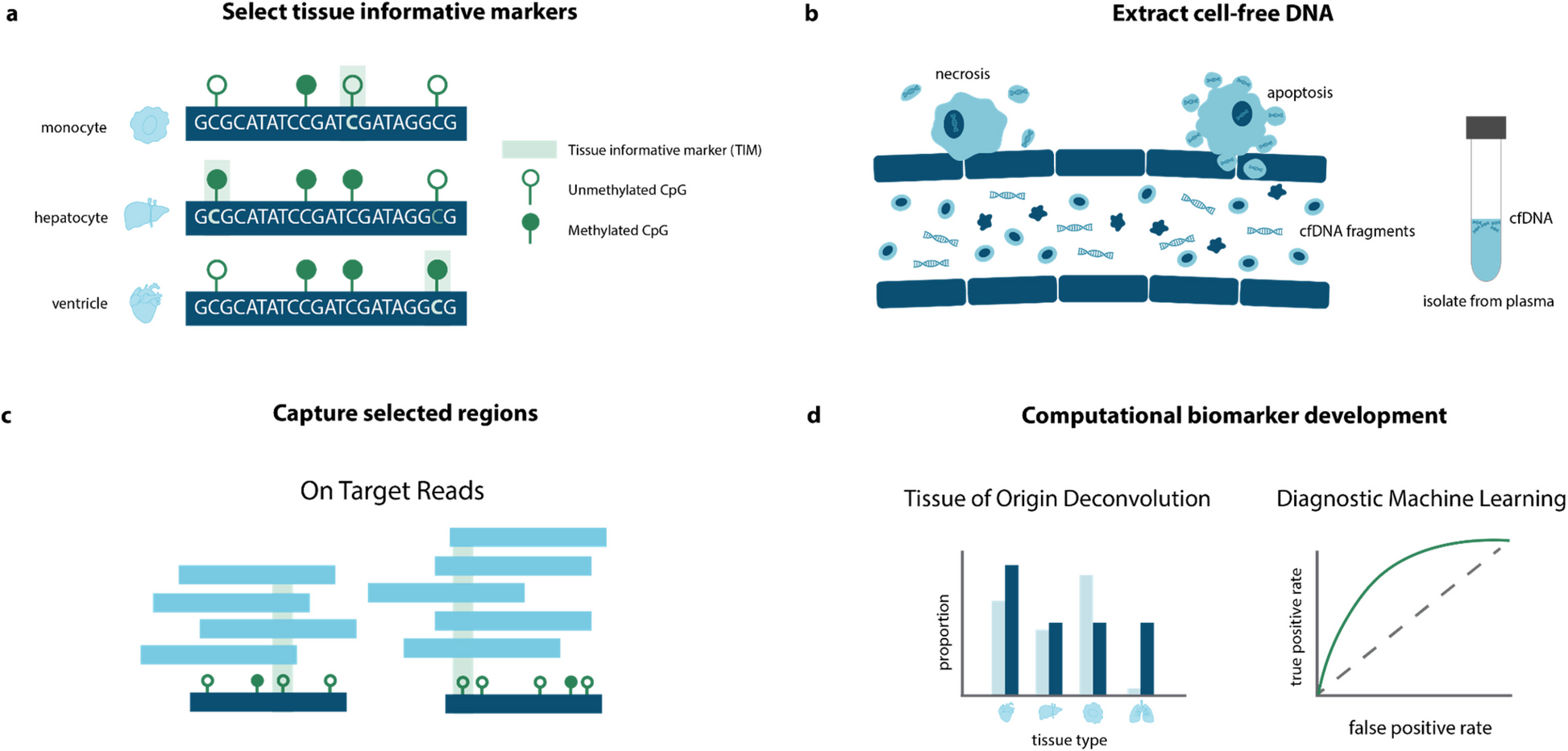
組織情報CpGのエピジェネティックプロファイルはALSの疾患状態と進行を知らせる Epigenetic profiles of tissue informative CpGs inform ALS disease status and progression
Christa Caggiano,Marco Morselli,Xiaoyu Qian,Barbara Celona,Michael J. Thompson,Shivangi Wani,Anela Tosevska,Kodi Taraszka,Galen Heuer,Shyuan T. Ngo,Frederick J. Steyn,Peter J. Nestor,Leanne Wallace,Pamela McCombe,Susan Heggie,Kathryn Thorpe,Caitlin McElligott,Gemyka English,Anjali Henders,Robert Henderson,Catherine Lomen-Hoerth,Naomi R. Wray,Allan F. McRae,Matteo Pellegrini,… Noah Zaitlen
Genome Medicine Published:16 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-025-01542-5
Abstract
Background
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA), derived from dying cells, has demonstrated utility across multiple clinical applications. However, its potential in neurodegenerative diseases remains underexplored, with most existing cfDNA technologies tailored to specific disease contexts like cancer or non-invasive prenatal screening.
Methods
To address this gap, we developed a novel approach to characterize epigenetic cfDNA profiles by identifying key regions of DNA methylation that reveal the tissues origins undergoing apoptosis or necrosis. We evaluated this method in the largest cfDNA study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other neurological diseases (OND) to date, encompassing two independent cohorts (n = 192) from Australia (UQ Ncases = 48, Ncontrols = 32, NOND = 15) and the USA, (UCSF Ncases = 50, Ncontrols = 45)).
Results
Our approach accurately distinguished ALS patients from controls (UQ AUC = 0.82, UCSF AUC = 0.99) and from individuals with other neurological diseases (AUC = 0.91). It also identified an asymptomatic carrier of a pathogenic C9orf72 variant, and strongly correlated with ALS disease progression measures (Pearson’s R = 0.66, p = 3.71 × 10⁻⁹).
Conclusions
We identified DNA methylation signals from multiple tissue types in ALS cfDNA, highlighting diverse tissue involvement in ALS pathology. These findings promote epigenetic cfDNA analysis as a powerful tool for advancing our understanding of neurodegenerative disease.