比較的短時間の被ばくで損傷を引き起こすことが、カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校の研究で明らかになった A relatively short exposure is sufficient to cause the damage, UC Riverside study finds
2022-06-08 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
ニコチンを主成分とするTHSは、呼気煙やタバコの先から出る煙が衣服、髪、家具、車などの表面に付着することで発生する。厳密には煙ではなく、THSは喫煙によって残された残留物のことを指します。電子タバコのこぼれは、電子タバコ製品の液漏れや、消費者と業者が詰め替え用電子タバコの電子液を混ぜた際に発生する可能性のある電子タバコの液漏れのことです。
研究成果は、雑誌「Atmosphere」に掲載されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2022/06/08/human-skin-can-be-damaged-exposure-thirdhand-smoke-and-electronic-cigarette
- https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/13/5/810
EpiDermTM器官型組織およびケラチノサイト単層におけるニコチンの複数の生物学的過程への影響 Nicotine Affects Multiple Biological Processes in EpiDermTM Organotypic Tissues and Keratinocyte Monolayers
Giovanna L. Pozuelos,Matine Rubin,Samantha Vargas,Erik Ramirez,Dhiresh Bandaru,Jihui Sha,James Wohlschlegel and Prue Talbot
Atmosphere Published: 16 May 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050810
Abstract
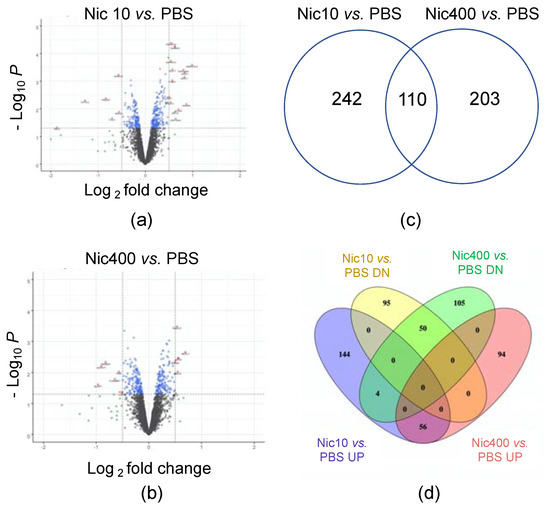
Dermal exposure to nicotine is common due to the widespread use of tobacco products. Here, we assessed the effects of nicotine at concentrations found in thirdhand smoke (THS) contaminated environments and electronic cigarette (EC) spills or leaks on a 3D human skin model (EpiDermTM) and on submerged keratinocyte cultures. Air liquid interface treatment of EpiDermTM with 10 or 400 μg/mL of nicotine for 24 h followed by proteomics analysis showed altered pathways related to inflammation, protein synthesis, cell–cell adhesion, apoptosis, and mitochondrial function. Submerged cultured keratinocytes were used to validate the proteomics data and further characterize the response of skin cells to nicotine. Mitochondrial phenotype changed from networked to punctate in keratinocytes treated with 10 or 400 μg/mL of nicotine for 48 h and 24 h, respectively. After 72 h, all concentrations of nicotine caused a significant decrease in the networked phenotype. In Western blots, keratinocytes exposed to 400 μg/mL of nicotine had a significant decrease in mitofusin 2, while mitofusin 1 decreased after 72 h. The shift from networked to punctate mitochondria correlated with a decrease in mitofusin 1/2, a protein needed to establish and maintain the networked phenotype. Mitochondrial changes were reversible after a 24 h recovery period. Peroxisomes exposed to 400 μg/mL of nicotine for 24 h became enlarged and were fewer in number. Nicotine concentrations in THS and EC spills altered the proteome profile in EpiDermTM and damaged organelles including mitochondria and peroxisomes, which are involved in ROS homeostasis. These changes may exacerbate skin infections, inhibit wound healing, and cause oxidative damage to cells in the skin.