2025-10-20 ヒューストン大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.uh.edu/news-events/stories/2025/october/10202025-woody-mda-cancer.php
- https://www.mdanderson.org/newsroom/research-newsroom/-esmo-2025–mrna-based-covid-vaccines-generate-improved-response.h00-159780390.html.
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09655-y
SARS-CoV-2 mRNAワクチンは腫瘍を免疫チェックポイント阻害に対して感受性化する SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines sensitize tumours to immune checkpoint blockade
Adam J. Grippin,Christiano Marconi,Sage Copling,Nan Li,Chen Braun,Cole Woody,Elliana Young,Priti Gupta,Min Wang,Annette Wu,Seong Dong Jeong,Dhruvkumar Soni,Frances Weidert,Chao Xie,Eden Goldenberg,Andrew Kim,Chong Zhao,Anna DeVries,Paul Castillo,Rishabh Lohray,Michael K. Rooney,Benjamin R. Schrank,Yifan Wang,Yifan Ma,D3CODE Team,… Steven H. Lin
Nature Published:22 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09655-y
Abstract
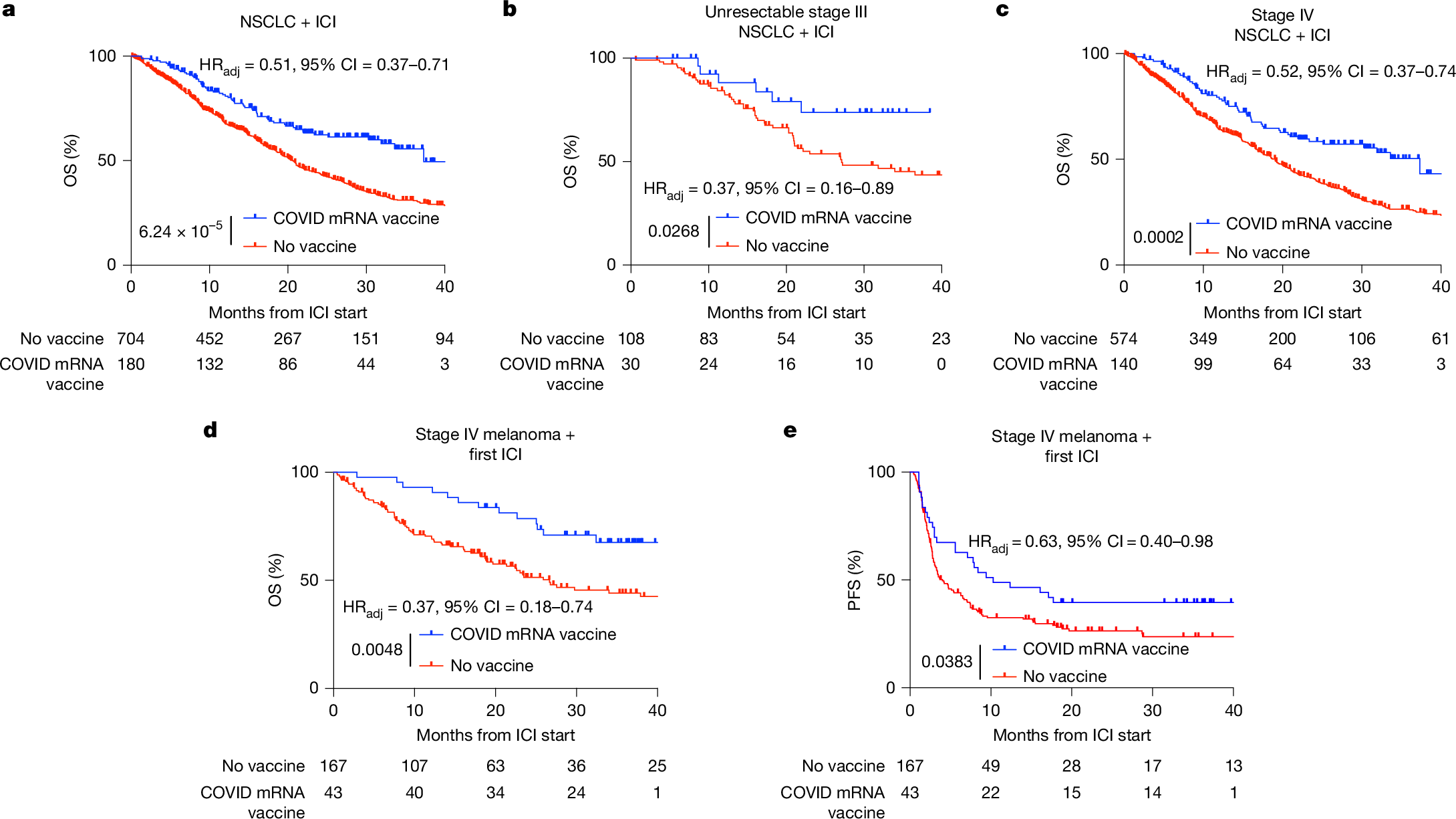
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) extend survival in many patients with cancer but are ineffective in patients without pre-existing immunity1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Although personalized mRNA cancer vaccines sensitize tumours to ICIs by directing immune attacks against preselected antigens, personalized vaccines are limited by complex and time-intensive manufacturing processes10,11,12,13,14. Here we show that mRNA vaccines targeting SARS-CoV-2 also sensitize tumours to ICIs. In preclinical models, SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines led to a substantial increase in type I interferon, enabling innate immune cells to prime CD8+ T cells that target tumour-associated antigens. Concomitant ICI treatment is required for maximal efficacy in immunologically cold tumours, which respond by increasing PD-L1 expression. Similar correlates of vaccination response are found in humans, including increases in type I interferon, myeloid–lymphoid activation in healthy volunteers and PD-L1 expression on tumours. Moreover, receipt of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines within 100 days of initiating ICI is associated with significantly improved median and three-year overall survival in multiple large retrospective cohorts. This benefit is similar among patients with immunologically cold tumours. Together, these results demonstrate that clinically available mRNA vaccines targeting non-tumour-related antigens are potent immune modulators capable of sensitizing tumours to ICIs.