2025-10-23 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/new-gene-discovery-aids-heart-disease-prevention
- https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cvr/cvaf177/8296653
マルチオミクスアプローチにより、IL6Rが亜臨床的頸動脈アテローム性動脈硬化症のエンドタイプに及ぼす因果関係とIL6R/OSMR経路の潜在的な役割が 明らかになった A multi-omics approach uncovers causality of IL6R on endotypes of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis and the possible role of the IL6R/OSMR pathway
Qiao Sen Chen, Hanna M Björck, Otto Bergman, Damiano Baldassarre, Gunnar Engström, Antonio Gallo, Anders Gummesson, Ulf Hedin, Sudhir Kurl, Lars Lind …
Cardiovascular Research Published:22 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaf177
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
Aims
Endotypes integrate individual clinical and molecular data and can be used to formulate molecular subclassifications of diseases. We previously derived four endotypes of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in a large European cohort, c-IMT and c-IMT Progression as Predictors of Vascular Events in a High-Risk European Population (IMPROVE), identifying individuals with a specific cardiovascular (CV) risk, ranging from low (endotype 1) to very high (endotype 4). Here, we investigate the mechanisms underlying the differences in CV risk observed across these four endotypes.
Methods and results
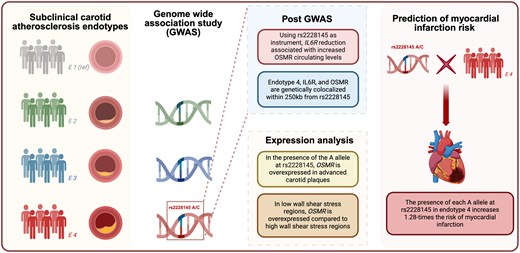
We validated the four endotypes in SCAPIS (n = 5050) and UK Biobank (n = 50 396) using carotid plaque and carotid intima-media thickness (c-IMT) as subclinical atherosclerosis measures. Endotype 4 associated with a larger number of carotid plaques and increased c-IMT measures as compared to endotype 1. We performed a meta-analysis of individual genome wide association studies in IMPROVE (n = 3711), SCAPIS and UK Biobank, and identified 12 SNPs associated with endotypes. We investigated if they regulated gene expression and circulating protein levels. We found that rs2228145A/C at Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL6R), associated with endotype 4, regulated IL6R expression and circulating levels of OncoStatin M Receptor (OSMR), Complement Factor B (CFB) and Fibrinogen Chain A (FGA). We used rs2228145A/C as an instrument in two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses and showed that a decreasing IL6R expression, associated with increasing CFB, FGA, and OSMR circulating levels. Endotype 4, IL6R, CFB, FGA, and OSMR co-localized within 250 kb surrounding rs2228145A/C. However, only OSMR was up-regulated in advanced carotid atherosclerotic plaques in the presence of the A allele and in aortic region exposed to low wall shear stress. In the UK Biobank, we observed that each additional A allele at rs2228145 increased by 1.28-times the risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in endotype 4.
Conclusion
Rs2228145A/C associated with endotype 4 clinical and molecular characteristics and amplified the MI risk in individuals assigned to endotype 4. These effects appeared to be mediated by a crosstalk with OSMR.


