2025-10-24 東京科学大学
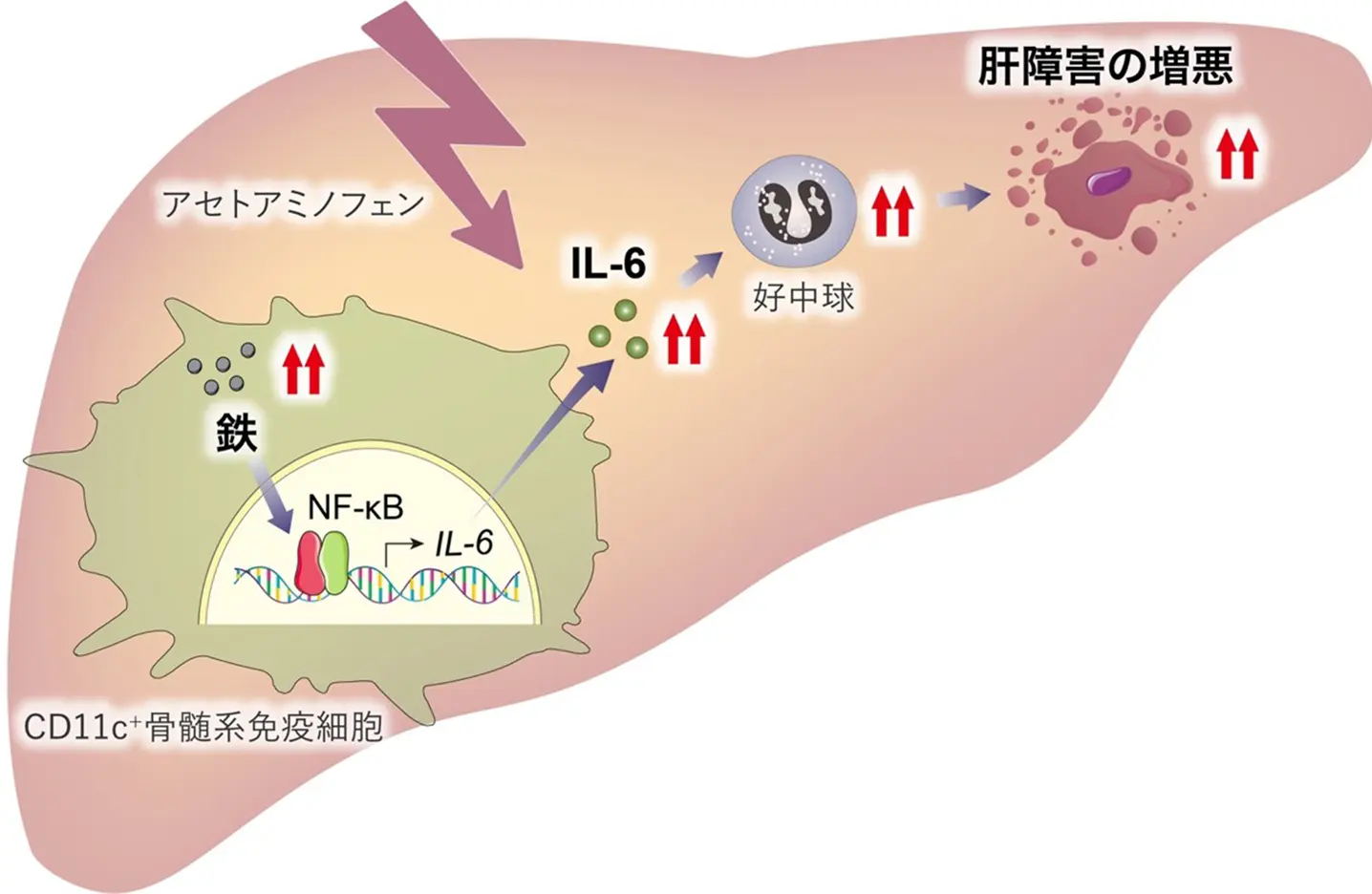
図 免疫細胞内の鉄過剰が薬剤性肝障害を悪化させるメカニズム
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/1uy6otj7ogoi
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2136&prevId=&key=0f74c64d152c574795cf120e2a72da28.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08521-x
CD11c +骨髄細胞における鉄過剰はアセトアミノフェンの肝毒性を悪化させる Iron overload in CD11c+ myeloid cells exacerbates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
Saisai Liu,Yohei Kanamori,Yudai Ohta,Shuran Li,Yanliang Liu,Hao Li,Mohamed Fathi Saleh,Akihiro Nita,Keiichi I. Nakayama & Toshiro Moroishi
Communications Biology Published:21 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-08521-x
Abstract
Acute liver injury often progresses to liver failure, with immune responses playing a critical role in regulating the inflammatory process. In this study, we aim to investigate the effects of iron on CD11c+ myeloid cells during acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Iron overload caused by F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (FBXL5) deficiency in CD11c+ cells exacerbates liver damage. CD11c+ myeloid cell-specific FBXL5-deficient mice exhibit higher serum transaminase levels, liver injury, and mortality than the controls. These phenotypes are associated with enhanced neutrophil infiltration and expression of interleukin (IL)-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine. Mechanistically, iron overload in FBXL5-deficient cells increases IL-6 production by facilitating the recruitment of nuclear factor-κB to the Il-6 promoter. In vivo, IL-6 neutralization mitigates liver injury, confirming its role in disease progression. Our findings highlight the role of iron in immune responses and suggest that targeting iron may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for liver injury.