2025-11-05 バース大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.bath.ac.uk/announcements/dna-discovery-could-help-identify-mothers-at-risk-of-pre-eclampsia/
- https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-025-03821-1
ERV3-MLT1はヒト胎盤機能のシス調節要素を提供し、ヒト特有の妊娠中毒症では一般的に調節不全となっている ERV3-MLT1 provides cis-regulatory elements for human placental functioning and are commonly dysregulated in human-specific preeclampsia
Rabia Anwar,Amit Pande,Manvendra Singh,Zhi Huang,Eve Hallett,Yiran Xie,Alexandra Gellhaus,Florian Herse,Olivia Nonn,Martin Gauster,Tamás Raskó,Matthias Selbach,Stefan Verlohren,Anne Cathrine Staff,Ralf Dechend,Ulrich Pecks,Sandra M. Blois,Laurence D. Hurst & Zsuzsanna Izsvák
Genome Biology Published:05 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-025-03821-1
Abstract
Background
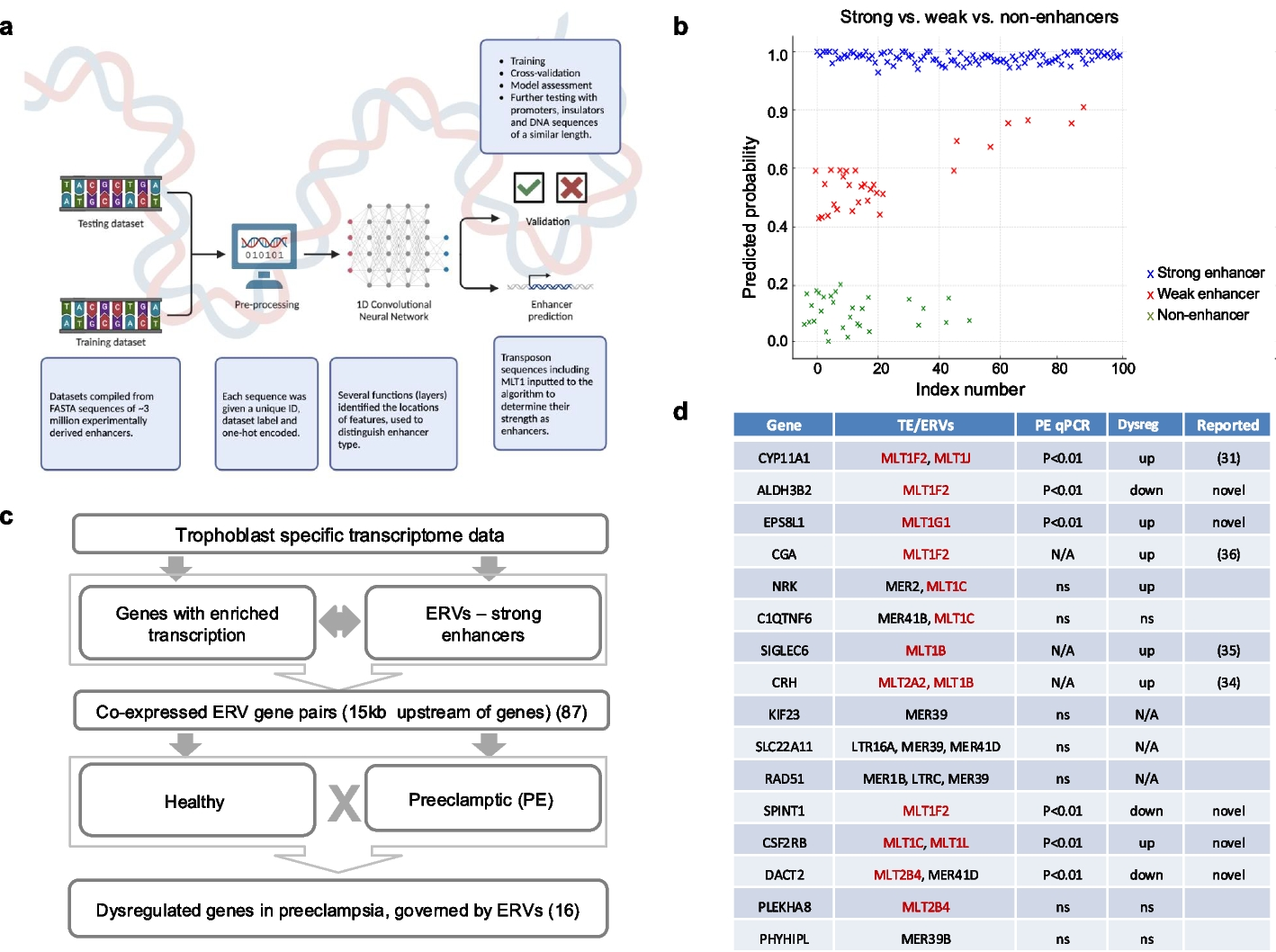
Owing to their transcription factor binding sites, endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) can act as cis-regulatory-elements (CREs). By invading genomes in waves, ERVs offer a substrate for lineage-specific adaptations but also, when dysregulated, for lineage-specific disorders. Their role as CREs in rapid placental evolution, and in the human-specific placental disorder preeclampsia, may thus provide a paradigmatic exemplar. Here then we systematically identify ERV-derived CREs controlling human placental gene expression with dysregulation in preeclampsia.
Results
We identify 87 ERV-derived CREs located upstream of genes expressed in the placenta. A subset of nine, all belonging to the ERV3-MLT1/2 families and dating to the mouse–human common ancestor, are consistently dysregulated in trophoblasts from preeclampsia samples. Of the nine ERV3-MLT1-linked genes dysregulated in preeclampsia, five are novel candidates, while four were previously associated with preeclampsia, though their ERV-based regulation was not recognized. Focusing on EPS8L1, we predict enhancer activity of upstream MLT1(G1) and validate using reporter assay and genome editing. This vertebrate-specific gene is expressed in progenitor cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts and is overexpressed in preeclampsia, correlating with preeclampsia biomarkers and is not elevated in related pregnancy disorders. A soluble form of EPS8L1 is detectable in maternal plasma as early as between 24 weeks of gestation. EPS8L1 knockout in trophoblast in vitro is lethal, and its overexpression alters trophoblast behaviors characteristic of preeclampsia.
Conclusions
We conclude that ERV3-MLT1functions as a trophoblast-specific CRE for several human genes and may be dysregulated in preeclampsia. As EPS8L1 has a form in maternal circulation, it may have utility in diagnostics.