2025-12-16 ヒューストン大学(UH)
<関連情報>
- https://www.uh.edu/news-events/stories/2025/december/12162025-muscle-wasting-cancer-kumar.php
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1038/s44321-025-00337-w
標準的なERストレスIRE1α/XBP1経路は膵臓癌悪液質中の骨格筋消耗を媒介する The canonical ER stress IRE1α/XBP1 pathway mediates skeletal muscle wasting during pancreatic cancer cachexia
Aniket S Joshi,Meiricris Tomaz da Silva,Anh Tuan Vuong,Bowen Xu,Ravi K Singh & Ashok Kumar
EMBO Molecular Medicine Published:17 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44321-025-00337-w
Abstract
Cancer cachexia is a debilitating syndrome characterized by the progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass with or without fat loss. Recent studies have implicated dysregulation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced unfolded protein response (UPR) pathways in skeletal muscle under various conditions, including cancer. In this study, we demonstrate that the IRE1α/XBP1 branch of the UPR promotes activation of the ubiquitin–proteasome system, autophagy, JAK-STAT3 signaling, and fatty acid metabolism in the skeletal muscle of the KPC mouse model of pancreatic cancer cachexia. Moreover, we show that the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway is a key contributor to muscle wasting. Skeletal muscle-specific deletion of the XBP1 transcription factor significantly attenuates tumor-induced muscle atrophy. Mechanistically, transcriptionally active XBP1 binds to the promoter regions of genes such as Map1lc3b, Fbxo32, and Il6, which encode proteins known to drive muscle proteolysis. Pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α using 4µ8C in KPC tumor-bearing mice attenuates cachexia-associated molecular changes and improves muscle mass and strength. Collectively, our findings suggest that targeting IRE1α/XBP1 pathway may offer a therapeutic strategy to counteract muscle wasting during pancreatic cancer-induced cachexia.
Synopsis
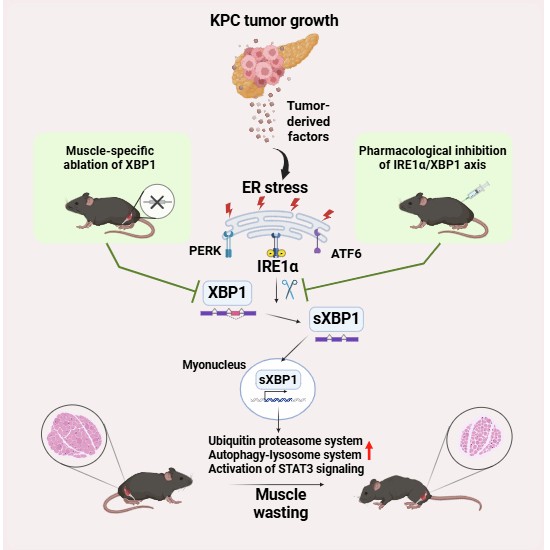
The study identifies the IRE1α/XBP1 arm of the ER stress-induced unfolded protein response as a key driver of skeletal muscle wasting and demonstrates that its genetic or pharmacological inhibition can attenuate the loss of skeletal muscle mass and function during pancreatic cancer-induced cachexia.
- The IRE1α/XBP1 arm of the unfolded protein response is activated in skeletal muscle during pancreatic cancer cachexia.
- Targeted deletion of XBP1 in mice counteracts the loss of skeletal muscle mass in response to tumor growth.
- XBP1 transcription factor augments the gene expression of key molecules involved in the regulation of proteolytic systems, STAT3 signaling, and fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle of tumor-bearing mice.
- Pharmacological inhibition of the IRE1α/XBP1 axis attenuates skeletal muscle wasting in response to pancreatic tumor growth.