2026-01-05 国立循環器病研究センター
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncvc.go.jp/hospital/topics/topics_36487/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JAHA.125.042387
脳内血腫の拡大を予測するための臨床応用可能な機械学習アプローチ Clinically Applicable Machine Learning Approach to Predict Intracerebral Hematoma Expansion
Shogo Watanabe, PhD, Nice Ren, MD, PhD, Yukihiro Imaoka, MD, PhD, Kento Morita, PhD, Syoji Kobashi, PhD, Nobutaka Mukae, MD, PhD, Koichi Arimura, MD, PhD, Kunihiro Nishimura, MD, PhD, and Koji Iihara, MD, PhD
Journal of the American Heart Association Published: 30 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.125.042387
Abstract
Background
Hematoma expansion (HE) is a significant risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Accurately predicting HE is crucial for determining optimal treatment strategies.
Methods
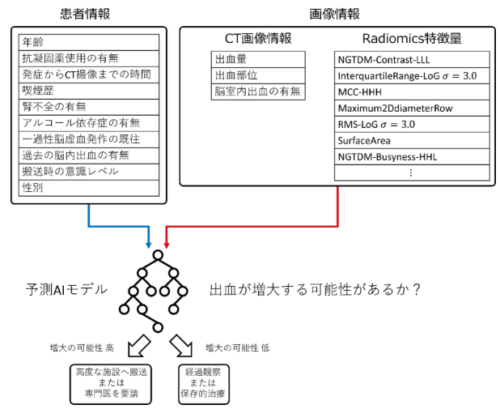
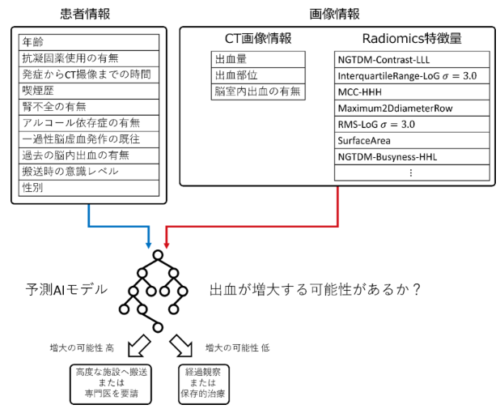
This study enrolled 452 patients with ICH from 10 hospitals. To predict HE, 28 clinical variables available on patient arrival (including medical history, ICH location, and ICH volume) and 1142 radiomics features extracted from noncontrast computed tomography images of the ICH regions were used. Clinical variables and radiomics features were selected using gradient boosting and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator. Three HE prediction models were built on clinical variables alone, radiomics features alone, and a third combining both. The models were compared using 5‐fold cross‐validation, and the mean area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was calculated for each. Additionally, the important features of HE prediction in the combined model were explored.
Results
The combined model demonstrated the highest performance for predicting HE with a 5‐fold mean area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.77±0.05, compared with 0.70±0.06 for the clinical variables alone and 0.73±0.04 for the radiomics features alone. Permutation feature importance analysis suggested that anticoagulant treatment was the most predictive of HE.
Conclusions
A predictive model for HE was developed using the medical history, clinical features available on the patient’s arrival, imaging, and radiomics features extracted from computed tomography images. This prediction model will assist non–stroke care specialists in making treatment decisions for ICH in emergency settings.