2026-01-14 東京大学
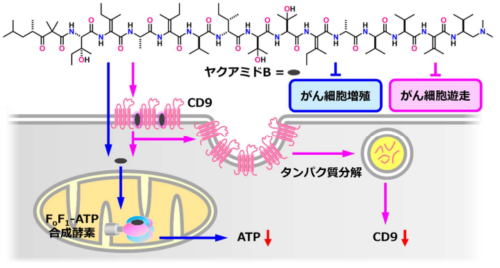
ヤクアミド B が示すがん細胞に対する二重作用(増殖抑制・遊走抑制)
<関連情報>
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/focus/ja/press/z0111_00096.html
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/content/400277938.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c13808
光親和性標識戦略によりテトラスパニンCD9が抗癌剤ヤクアミドBの一時的な標的であることが明らかになった Photoaffinity Labeling Strategy Reveals Tetraspanin CD9 as a Transient Target of Anticancer Yaku’amide B
Junhao Fu,Koichi Kamiya,Kai Kitamura,Ryo Kawahara,Wataru Shihoya,Osamu Nureki,Shoichi Hosoya,Reiko Nakagawa,Tetsuo Mashima,Hiroaki Itoh,Masayuki Inoue,and Kaori Sakurai
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: January 9, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c13808
Abstract
Innovative chemical strategies are needed to understand the molecular targets of natural products, especially when they engage with multiple targets via transient interactions. Yaku’amide B (1), an anticancer natural product, inhibits mitochondrial FoF1-ATP synthase with nanomolar affinity; however, this mechanism alone does not explain its unique activity. Here, we employed photoaffinity labeling (PAL), a powerful, chemical strategy, to discover that tetraspanin CD9 is a transient cell surface target of 1 in cancer cells. Comprehensive analyses revealed that 1 binds to the cytoplasmic N-terminal region of CD9 with micromolar affinity, which accelerates its cellular entry, inducing CD9 depletion via lysosomal proteolysis. Both 1 and siCD9 inhibit cancer cell migration, suggesting that the 1–CD9 interaction plays a role in the mechanism of action of 1. Thus, 1 represents a novel natural product that binds to and promotes the degradation of CD9. This study underscores the versatility of applying the PAL strategy for mechanistic studies and highlights 1 as a promising molecular platform for targeting CD9-mediated cellular pathways.


