2026-01-27 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)

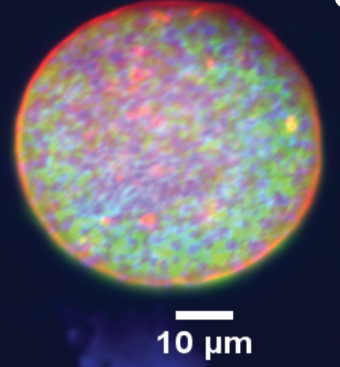
Hearing researchers require detailed images of stereocilia, the bundles of protrusions that detect sound and movement. The red hairs featured on the right were rescued to full length due to gene therapy, while green-intermediate hairs received partial treatment and blue received no treatment.
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/new-ai-tool-accelerates-hearing-research-with-unprecedented-3d-views-of-sensory-cells
- https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3003591
VASCiliaは、蝸牛有毛細胞のステレオシリア束の3D解析のためのオープンソースのディープラーニングベースのツールです VASCilia is an open-source, deep learning-based tool for 3D analysis of cochlear hair cell stereocilia bundles
Yasmin M. Kassim,David B. Rosenberg,Samprita Das,Xiaobo Wang,Zhuoling Huang,Samia Rahman,Ibraheem M. Al Shammaa,Samer Salim,Kevin Huang,Alma Renero,Yuzuru Ninoyu,Rick A. Friedman,Artur A. Indzhykulian,Uri Manor
PLOS Biology Published: January 20, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3003591
Abstract
Cochlear hair cells are essential for hearing, and their stereocilia bundles are critical for mechanotransduction. However, analyzing the 3D morphology of these bundles can be challenging due to their complex organization and the presence of other cellular structures in the tissue. To address this, we developed VASCilia (Vision Analysis StereoCilia), a Napari plugin suite that automates the analysis of 3D confocal microscopy datasets of phalloidin-stained cochlear hair cell bundles. VASCilia includes five deep learning-based models trained on mouse cochlear datasets that streamline the analysis process, including: (1) Z-Focus Tracker (ZFT) for selecting relevant slices in a 3D image stack; (2) PCPAlignNet (Planar Cell Polarity Alignment Network) for automated orientation of image stacks; (3) a segmentation model for identifying and delineating stereocilia bundles; (4) a tonotopic Position Prediction tool; and (5) a classification tool for identifying hair cell subtypes. In addition, VASCilia provides automated computational tools and measurement capabilities. Using VASCilia, we demonstrate its utility on challenging datasets, including neonatal wild type and Eps8 KO 5-day old mice. We further showcase its power by quantifying complex bundle disorganization in Cdh23-/- cochleae via texture analysis, which revealed systematically more heterogeneous and less regular bundles than littermate controls. These case studies demonstrate the power of VASCilia in facilitating detailed quantitative analysis of stereocilia. VASCilia also provides a user-friendly interface that allows researchers to easily navigate and use the tool, with the added capability to reload all their analyses for review or sharing purposes. We believe that VASCilia will be a valuable resource for researchers studying cochlear hair cell development and function, addressing a longstanding need in the hair cell research community for specialized deep learning-based tools capable of high-throughput image quantitation. We have released our code along with a manually annotated dataset that includes approximately 55 3D stacks featuring instance segmentation (https://github.com/ucsdmanorlab/Napari-VASCilia). This dataset comprises a total of 502 inner and 1,703 outer hair cell bundles annotated in 3D. As the first open-source dataset of its kind, we aim to establish a foundational resource for constructing a comprehensive atlas of cochlea hair cell images. Ultimately, this initiative will support the development of foundational models adaptable to various species, markers, and imaging scales to accelerate advances within the hearing research community.