2026-02-18 東京科学大学
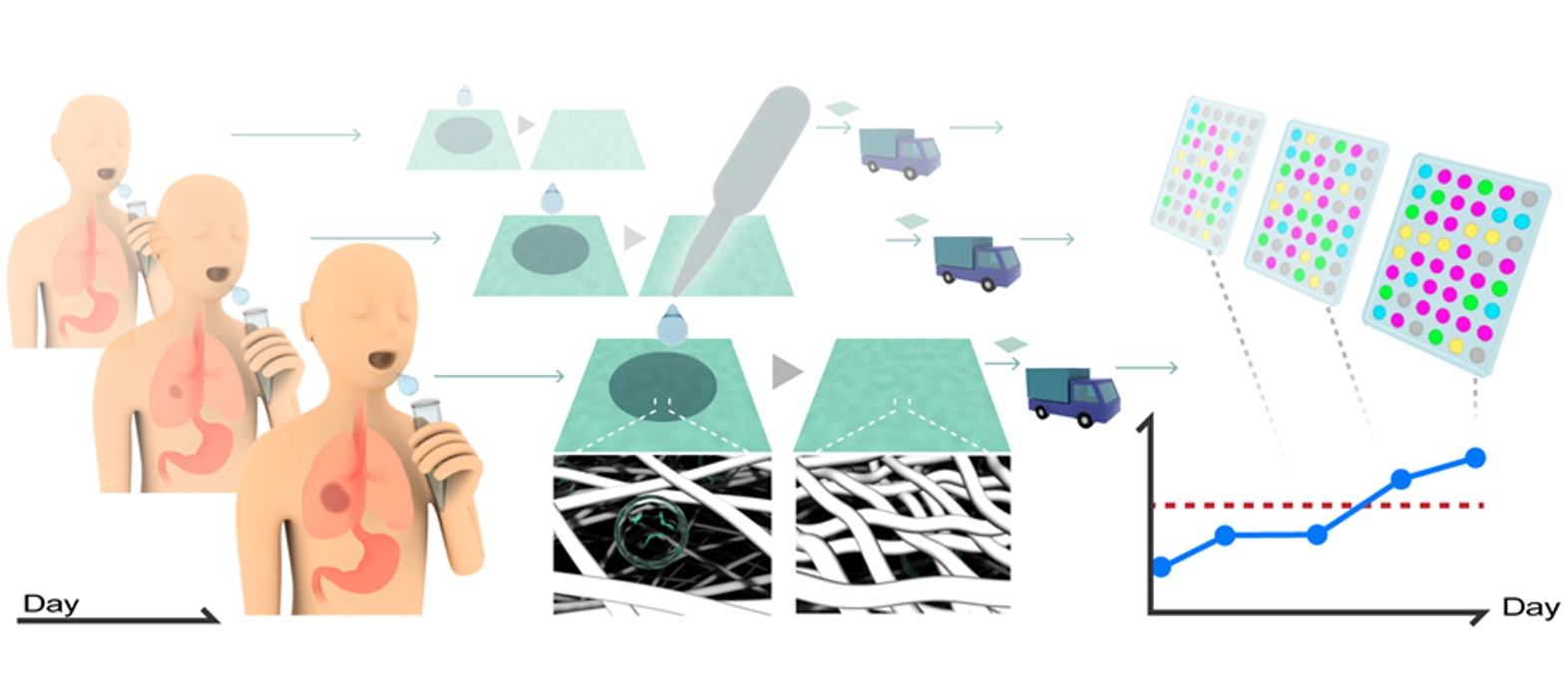
図1.本研究のコンセプト概略図。採取した唾液をセルロースナノファイバーシートに滴下して乾燥させ、そのシートを測定機関に送付することで、エクソソーム由来 microRNA を解析する。ユーザー側の操作は、「唾液をシートに載せて乾かすだけ」であり、この簡便な手順によって、日常的な microRNA 解析に基づくがんリスクモニタリングの実現を目指している。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/bw3c89hh4hto
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566326000680
セルロースナノファイバーシートを用いた唾液エクソソーム中のマイクロRNAの日常モニタリング Routine monitoring of microRNAs in salivary exosomes using a cellulose nanofiber sheet
Taiga Ajiri, Min Zhang, Naoya Mizukami, Mikiko Iida, Shota Kawaguchi, Yurie Sekihara, Kunanon Chattrairat, Zetao Zhu, Yoshinobu Baba, Hirotaka Koga, Takao Yasui
Biosensors and Bioelectronics Available online: 22 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2026.118436
Highlights
- Developed a CNF sheet as a simple and rapid platform for salivary EV capture and miRNA preservation.
- Optimized saliva sample processing conditions including volume, washing, and drying parameters.
- Demonstrated room temperature storage of EV miRNAs for at least six days without degradation.
- Identified cancer-associated salivary miRNA signatures and demonstrated feasibility of longitudinal daily monitoring.
Abstract
Liquid biopsy is a promising approach for non-invasive disease monitoring, offering the potential for frequent sampling and early risk assessment. Among various biofluids, saliva is particularly well-suited for daily sampling due to its ease of collection and minimal invasiveness. Here, we present a cellulose nanofiber sheet as a novel platform for the rapid, low-volume recovery and stable storage of miRNAs associated with small extracellular vesicles in saliva. The sheet captures vesicles via its nanoscale porous networks and preserves their contents at room temperature, enabling efficient extraction of vesicle-associated miRNAs. Compared to ultracentrifugation, the method demonstrated superior miRNA recovery and required only 10 μL of saliva and less than 1 min of processing. Analysis of salivary miRNA profiles from healthy individuals and cancer patients revealed distinct expression patterns, enabling identification of candidate cancer-related miRNAs. Furthermore, daily saliva sampling during 20 days demonstrated the feasibility of longitudinal miRNA profiling and highlighted the effects of factors such as food intake. These findings underscore the potential of cellulose nanofiber sheets as a practical tool for salivary miRNA monitoring, with applications in personalized health management, early risk detection, and decentralized testing environments.


