2026-02-18 東京大学
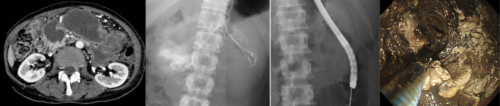
急性膵炎後 WON と WON に対する内視鏡治療
<関連情報>
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/20260218.html
- https://www.h.u-tokyo.ac.jp/press/__icsFiles/afieldfile/2026/02/18/release_20260218.pdf
- https://www.gastrojournal.org/article/S0016-5085(26)00118-6/abstract
壊死性膵炎に対する即時またはオンデマンド内視鏡的壊死切除術:ランダム化比較試験(WONDER-01) Immediate or On-Demand Endoscopic Necrosectomy for Necrotizing Pancreatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial (WONDER-01)
Tomotaka Saito, MD, PhD ∙ Toshio Fujisawa, MD, PhD ∙ Takeshi Ogura, MD, PhD ∙ … ∙ Ichiro Yasuda, MD, PhD ∙ Yousuke Nakai, MD, PhD the WONDERFUL study group in Japan and collaborators
Gastroenterology Published: February 17, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2026.01.034
Abstract
BACKGROUND & AIMS
The optimal timing for direct endoscopic necrosectomy (DEN) following endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transmural drainage of symptomatic necrotizing pancreatitis remains unknown. We hypothesized that immediate DEN following EUS-guided drainage might reduce the time to disease resolution compared with a drainage-oriented step-up approach.
METHODS
This study was a multicenter, open-label, superiority randomized trial (WONDER-01). Among patients who received EUS-guided treatment for symptomatic necrotizing pancreatitis, eligible patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either immediate DEN or the drainage-oriented step-up approach. The primary endpoint was the time from randomization to clinical success, defined as a decrease in collection size to ≤3 cm and an improvement in inflammatory markers.
RESULTS
Seventy patients were enrolled in this study: 33 in the immediate DEN arm and 37 in the step-up arm. Immediate DEN was associated with a shorter time to clinical success than the step-up approach (P = .009), with median times (95% confidence interval) of 29 (19–34) and 44 (38–52) days, respectively. All patients in the immediate DEN arm received DEN compared to 46% in the step-up approach arm, but the rates of procedure-related adverse events were comparable (24% vs 22%, respectively; P = .79). No significant differences were noted between the treatment arms in terms of technical success (100% vs 97%, P > .99) and mortality (12% vs 5.4%, P = .41).
CONCLUSION
Compared with the step-up approach, immediate DEN following EUS-guided drainage of necrotizing pancreatitis reduced time to clinical success without increasing adverse outcomes but required more DEN procedures (ClinicalTrials.gov, Number: NCT05451901).


