2022-06-02 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
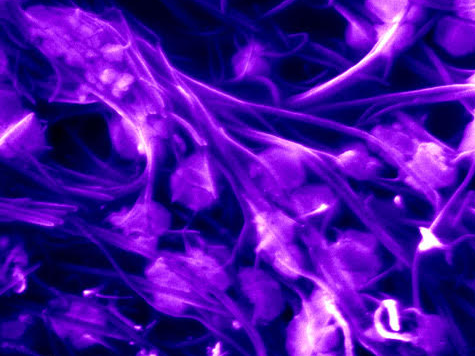
Scanning electron microscopy image showing carbon nanotubes (purple) effectively trapping Influenza viruses (light purple round objects). These trapped viruses are then analyzed by Raman spectroscopy and machine learning and they can be identified with accuracies >95%. Credit: Elizabeth Floresgomez and Yin-Ting Yeh. All Rights Reserved.
このウイルス検出方法は、ラベルフリーで、特定のウイルスを対象としないため、新種のウイルスの可能性を特定することができます。
また、迅速であるため、混雑した公共空間での迅速なスクリーニングに適しています。さらに、豊富なラマンの特徴と機械学習による解析が、ウイルスの構造をより深く理解することを可能にします。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/materials-research-institute/story/real-time-accurate-virus-detection-method-could-help-fight-next/
- https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2118836119
機械学習による解釈可能なラマンシグネチャを用いたウイルスの高精度な同定 Accurate virus identification with interpretable Raman signatures by machine learning
Jiarong Ye, Yin-Ting Yeh , Yuan Xue , Ziyang Wang, Na Zhang, He Liu, Kunyan Zhang, RyeAnne Ricker, Zhuohang Yu, Allison Roder, Nestor Perea Lopez, Lindsey Organtini, Wallace Greene, Susan Hafenstein, Huaguang Lu, Elodie Ghedin, Mauricio Terrones, Shengxi Huang, and Sharon Xiaolei Huang
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Published:June 2, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2118836119
Abstract
Rapid identification of newly emerging or circulating viruses is an important first step toward managing the public health response to potential outbreaks. A portable virus capture device, coupled with label-free Raman spectroscopy, holds the promise of fast detection by rapidly obtaining the Raman signature of a virus followed by a machine learning (ML) approach applied to recognize the virus based on its Raman spectrum, which is used as a fingerprint. We present such an ML approach for analyzing Raman spectra of human and avian viruses. A convolutional neural network (CNN) classifier specifically designed for spectral data achieves very high accuracy for a variety of virus type or subtype identification tasks. In particular, it achieves 99% accuracy for classifying influenza virus type A versus type B, 96% accuracy for classifying four subtypes of influenza A, 95% accuracy for differentiating enveloped and nonenveloped viruses, and 99% accuracy for differentiating avian coronavirus (infectious bronchitis virus [IBV]) from other avian viruses. Furthermore, interpretation of neural net responses in the trained CNN model using a full-gradient algorithm highlights Raman spectral ranges that are most important to virus identification. By correlating ML-selected salient Raman ranges with the signature ranges of known biomolecules and chemical functional groups—for example, amide, amino acid, and carboxylic acid—we verify that our ML model effectively recognizes the Raman signatures of proteins, lipids, and other vital functional groups present in different viruses and uses a weighted combination of these signatures to identify viruses.