遺伝子発現予測を改善し、COVID-19などヒト疾患治療への再利用が可能な薬剤を特定する新規手法を開発 Novel approach improves gene expression prediction and identifies drugs that may be repurposed for treating human diseases, including COVID-19
2022-06-28 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
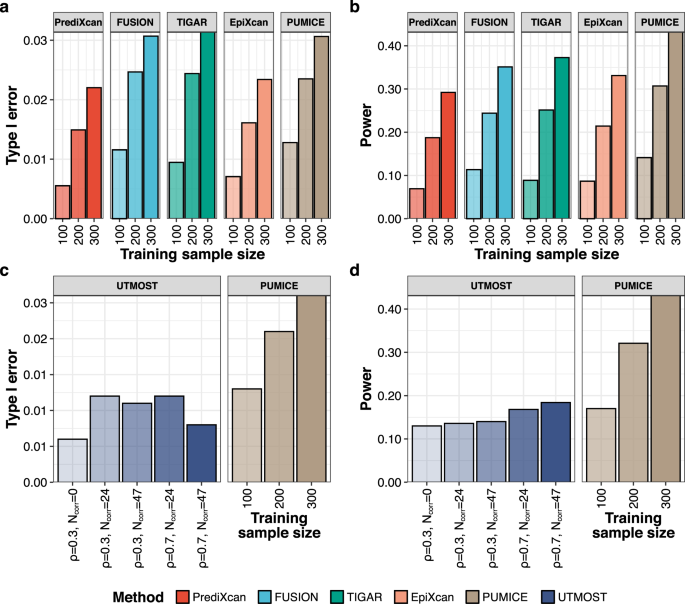
新しいデータ手法であるPUMICE(Prediction Using Models Informed by Chromatin conformations and Epigenomics)では、ペンシルベニア州立大学の研究者が、新しい機械学習アプローチを用いてトランスクリプトーム、エピゲノムおよび3Dゲノムデータを統合しました。この研究によると、PUMICEは疾患遺伝子の発現レベルを逆転させる薬剤の同定に成功し、いくつかのヒト疾患の治療に再利用できる可能性があるとのことです。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/new-machine-learning-technique-shows-how-drugs-can-be-repurposed/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30956-7
トランスクリプトームワイドアソシエーション研究における標的遺伝子探索と薬剤リパーポージングを強化するための3Dゲノムおよびエピゲノムデータの統合 Integrating 3D genomic and epigenomic data to enhance target gene discovery and drug repurposing in transcriptome-wide association studies
Chachrit Khunsriraksakul,Daniel McGuire,Renan Sauteraud,Fang Chen,Lina Yang,Lida Wang,Jordan Hughey,Scott Eckert,J. Dylan Weissenkampen,Ganesh Shenoy,Olivia Marx,Laura Carrel,Bibo Jiang & Dajiang J. Liu
Nature Communications Published:07 June 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30956-7
Abstract
Transcriptome-wide association studies (TWAS) are popular approaches to test for association between imputed gene expression levels and traits of interest. Here, we propose an integrative method PUMICE (Prediction Using Models Informed by Chromatin conformations and Epigenomics) to integrate 3D genomic and epigenomic data with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) to more accurately predict gene expressions. PUMICE helps define and prioritize regions that harbor cis-regulatory variants, which outperforms competing methods. We further describe an extension to our method PUMICE +, which jointly combines TWAS results from single- and multi-tissue models. Across 79 traits, PUMICE + identifies 22% more independent novel genes and increases median chi-square statistics values at known loci by 35% compared to the second-best method, as well as achieves the narrowest credible interval size. Lastly, we perform computational drug repurposing and confirm that PUMICE + outperforms other TWAS methods.