この人工知能モデルを活用することで、皮膚がん患者様により効果的な治療が可能になり、他のがんの診断や治療にも同様のブレークスルーがもたらされる可能性があります。 The artificial intelligence model could be utilized to enable more effective care for skin cancer patients and could lead to similar breakthroughs in the diagnosis and treatment of other cancers.
2022-10-12 フィンランド・アールト大学
研究グループはAIモデルを使って、約500人の皮膚がん患者のサンプルを分析し、約1,000人の健康な人のサンプルと比較した。また、解釈を助けるために、スタンフォード大学のマーク・M・デイビス研究室が開発した別のAIモデルも使用した。これらのサンプルから、研究者たちは、皮膚がんを認識する免疫細胞の数を単純に計算した。
予想通り、メラノーマ患者には、健康な患者よりも皮膚がんを感知する防御細胞が多く見受けられた。
この発見により、将来的には血液サンプルから皮膚がんを識別できるようになるかもしれない。
皮膚がんを認識する防御細胞が多い皮膚がん患者は、そのような細胞がない患者よりも、免疫系を活性化する治療法が有効である可能性が高いことも分かった。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aalto.fi/en/news/an-ai-model-reveals-how-the-bodys-defence-system-recognises-skin-cancer
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-33720-z
メラノーマ患者における抗原特異的T細胞応答の進化と変調 Evolution and modulation of antigen-specific T cell responses in melanoma patients
Jani Huuhtanen,Liang Chen,Emmi Jokinen,Henna Kasanen,Tapio Lönnberg,Anna Kreutzman,Katriina Peltola,Micaela Hernberg,Chunlin Wang,Cassian Yee,Harri Lähdesmäki,Mark M. Davis & Satu Mustjoki
Nature Communications Published:11 October 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33720-z
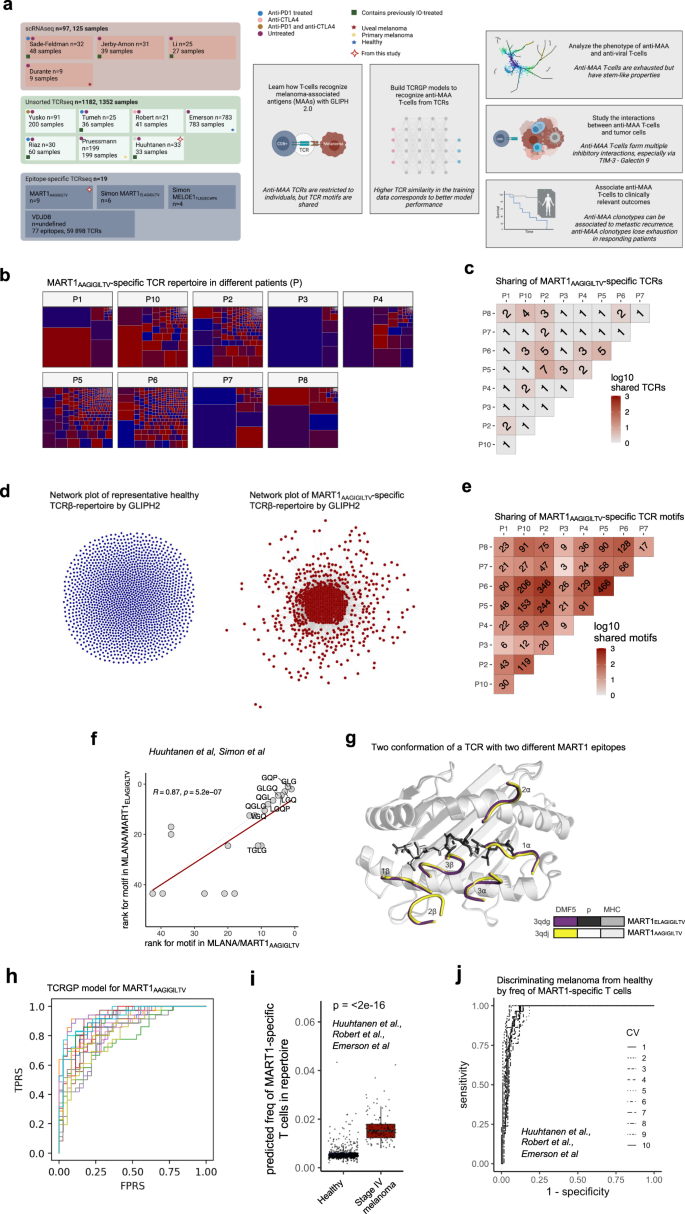
Abstract
Analyzing antigen-specific T cell responses at scale has been challenging. Here, we analyze three types of T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire data (antigen-specific TCRs, TCR-repertoire, and single-cell RNA + TCRαβ-sequencing data) from 515 patients with primary or metastatic melanoma and compare it to 783 healthy controls. Although melanoma-associated antigen (MAA) -specific TCRs are restricted to individuals, they share sequence similarities that allow us to build classifiers for predicting anti-MAA T cells. The frequency of anti-MAA T cells distinguishes melanoma patients from healthy and predicts metastatic recurrence from primary melanoma. Anti-MAA T cells have stem-like properties and frequent interactions with regulatory T cells and tumor cells via Galectin9-TIM3 and PVR–TIGIT -axes, respectively. In the responding patients, the number of expanded anti-MAA clones are higher after the anti-PD1(+anti-CTLA4) therapy and the exhaustion phenotype is rescued. Our systems immunology approach paves the way for understanding antigen-specific responses in human disorders.


