2023-08-31 エディンバラ大学
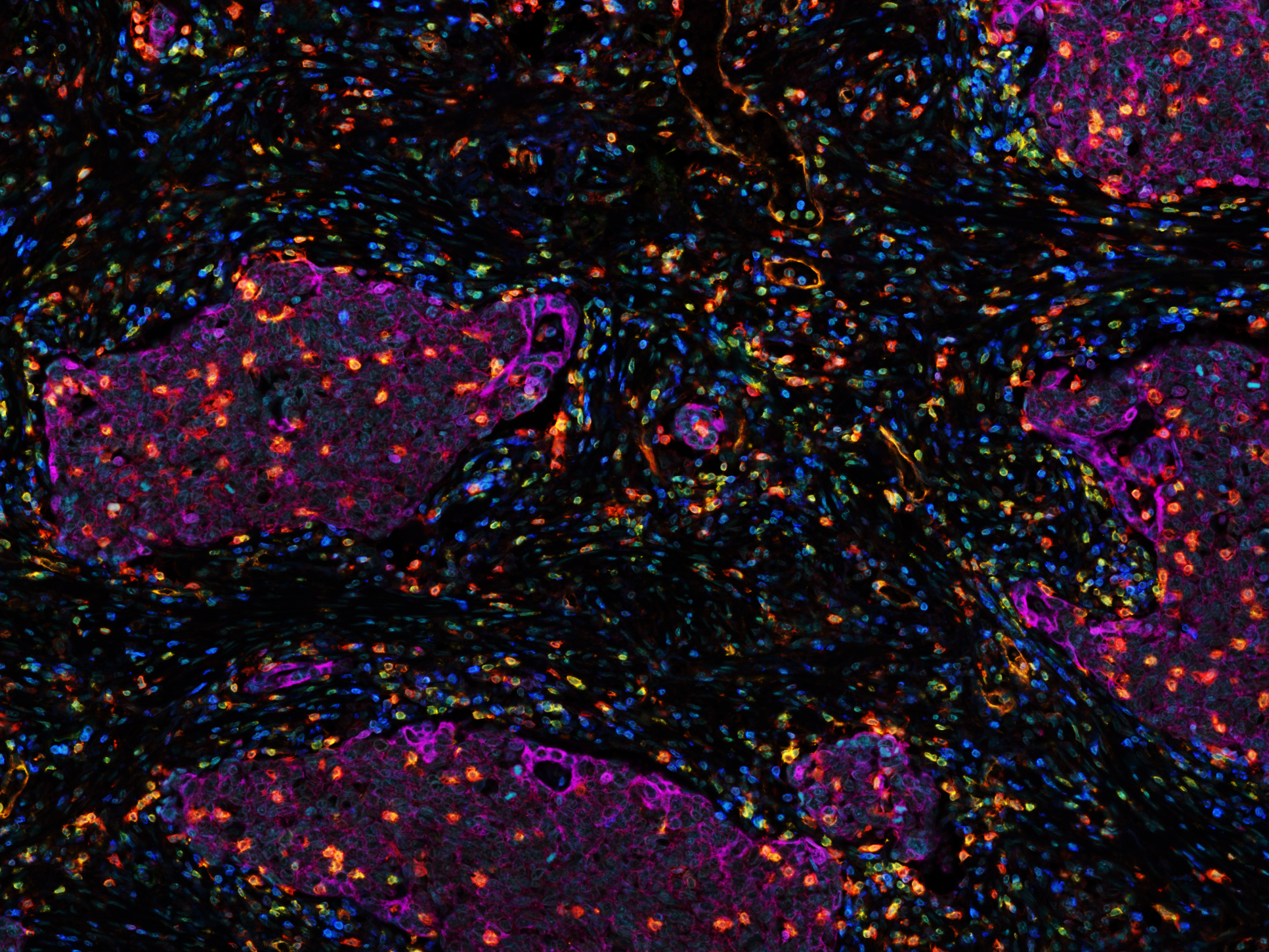
Clusters of lung cancer cells, known as the tumour nests (purple), infiltrated by cytotoxic T cells (orange)
◆肺がんに焦点を当てた研究では、免疫療法の不成功の原因を解明し、T細胞の活性を抑制するメカニズムを理解し、治療の効果を向上させる手段を模索しています。この研究により、がん患者にとってより効果的な治療法の開発に寄与する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/2023/blood-cell-insights-could-boost-lung
- https://jitc.bmj.com/content/11/8/e006770.info
腫瘍内のCD39+ T細胞亜集団の位置が、非小細胞肺癌における転帰の違いを予測する Location of CD39+ T cell subpopulations within tumors predict differential outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer
Lilian Koppensteiner,Layla Mathieson,Samuel Pattle,David A Dorward,Richard O’Connor and Ahsan R Akram
Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer Published: August 30, 2023.
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2023-006770
Abstract
Purpose An improved mechanistic understanding of immunosuppressive pathways in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is important to develop novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Here, we investigate the prognostic significance of the ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 in NSCLC.
Experimental design The expression and localization of CD39, CD73 and CD103 was digitally quantified in a cohort of 162 early treatment naïve NSCLC patients using multiplex-immunofluorescence and related to patient outcome. Expression among different cell-populations was assessed via flow cytometry. Targeted RNA-Seq was performed on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from digested NSCLC tumor tissue and single-cell RNA-Seq data was analyzed to investigate the functional significance of CD39+ T cell populations.
Results We demonstrate that flow cytometry of early untreated NSCLC patients shows an upregulation of CD39 expression in the tumor tissue among natural killer (NK) cells, fibroblasts and T cells. CD73 expression is mainly found among fibroblasts and Epcam+cells in the tumor tissue. Multiplex Immunofluorescence in a cohort of 162 early untreated NSCLC patients demonstrates that CD39 expression is mainly localized in the tumor stroma while CD73 expression is equally distributed between tumor nest and stroma, and high expression of CD39 and CD73 in the tumor stroma is associated with poor recurrence-free survival (RFS) at 5 years. Additionally, we find that CD8+T cells located in the tumor nest express CD103 and the density of CD39+CD103+CD8+ T cells in the tumor nest predicts improved RFS at 5 years. Targeted RNA-Seq shows that the tumor microenvironment of NSCLC upregulates regulatory pathways in CD4+ T cells and exhaustion in CD8+ T cells, and analysis of a single cell RNA sequencing dataset shows that CD39+CD4+ cells are enriched in Treg signature gene-sets, and CD39+CD103+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte show gene signatures indicative of an exhausted cytotoxic phenotype with upregulated expression of CXCL13.
Conclusions Knowledge of patterns of distribution and location are required to understand the prognostic impact of CD39+ T cell populations in NSCLC. This study provides an improved understanding of spatial and functional characteristics of CD39+ T cells and their significance to patient outcome.