2023-11-01 マックス・プランク研究所
◆この研究では、カスタマイズされたワークフローを使用して心筋サンプルの高解像度画像を生成し、筋肉タンパク質の3D組織に新たな洞察を提供しました。研究により、ミオシンがアクチンに結合し筋肉収縮を制御し、ネビュリンがアクチンに結合して安定化し長さを決定する方法など、サルコメア内の筋肉タンパク質の構造と機能についての理解が深まりました。
◆将来的には、異なる状態での分析や疾患患者のサンプルとの比較によって、高血圧性心筋症などの疾患の理解と新しい治療法の開発に寄与することが期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/21017835/1030-moph-breakthrough-discovery-sheds-light-on-heart-and-muscle-health-151445-x
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06690-5
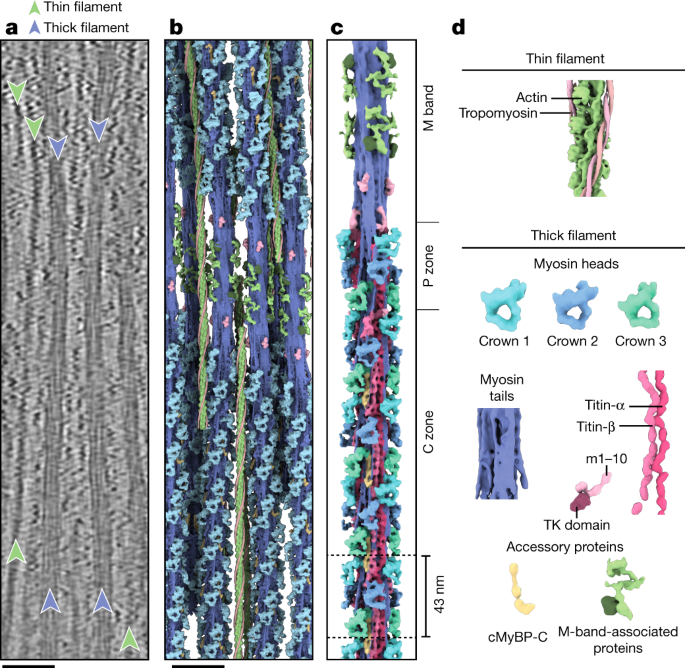
弛緩した心筋サルコメアのミオシンフィラメントの構造 Structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere
Davide Tamborrini,Zhexin Wang,Thorsten Wagner,Sebastian Tacke,Markus Stabrin,Michael Grange,Ay Lin Kho,Martin Rees,Pauline Bennett,Mathias Gautel & Stefan Raunser
Nature Published:01 November 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06690-5
Abstract
The thick filament is a key component of sarcomeres, the basic units of striated muscle1. Alterations in thick filament proteins are associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and other heart and muscle diseases2. Despite the central importance of the thick filament, its molecular organization remains unclear. Here we present the molecular architecture of native cardiac sarcomeres in the relaxed state, determined by cryo-electron tomography. Our reconstruction of the thick filament reveals the three-dimensional organization of myosin, titin and myosin-binding protein C (MyBP-C). The arrangement of myosin molecules is dependent on their position along the filament, suggesting specialized capacities in terms of strain susceptibility and force generation. Three pairs of titin-α and titin-β chains run axially along the filament, intertwining with myosin tails and probably orchestrating the length-dependent activation of the sarcomere. Notably, whereas the three titin-α chains run along the entire length of the thick filament, titin-β chains do not. The structure also demonstrates that MyBP-C bridges thin and thick filaments, with its carboxy-terminal region binding to the myosin tails and directly stabilizing the OFF state of the myosin heads in an unforeseen manner. These results provide a foundation for future research investigating muscle disorders involving sarcomeric components.