2023-12-08 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
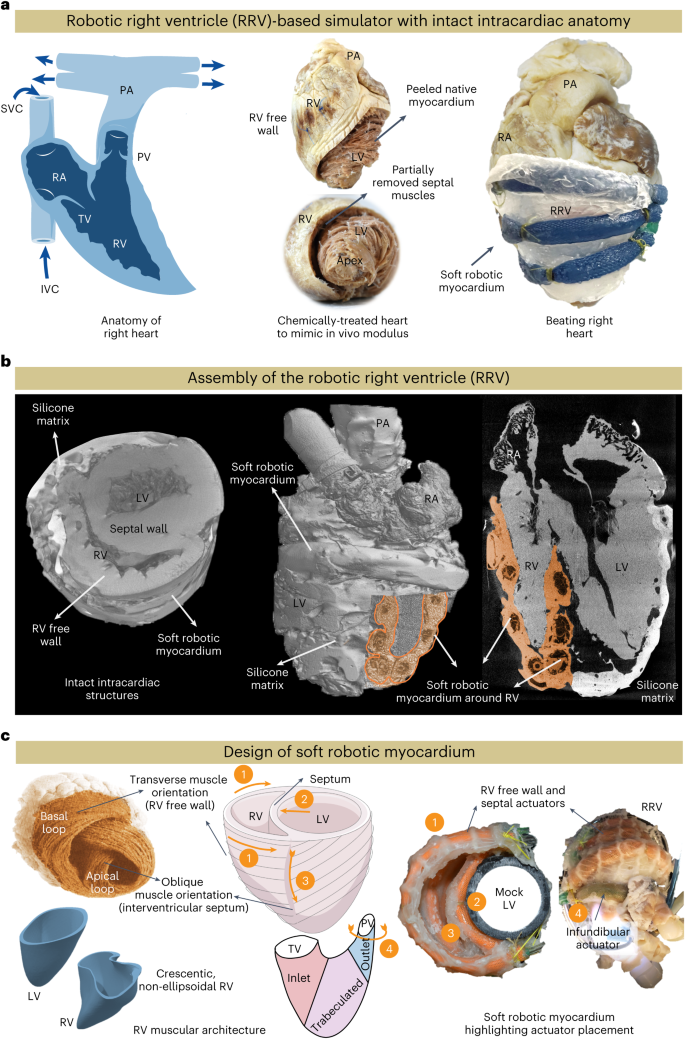
◆この人工心室は、健康な状態と病態を模倣するように調整でき、右心室の異常を研究し、それらの異常を治療するためのデバイスと治療法をテストするための実用的なプラットフォームとして使用できます。
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2023/mit-engineers-design-robotic-replica-hearts-right-chamber-1208
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44161-023-00387-8
ロボット右心室は、(病的)生理学的条件下での右心室機能をシミュレートし、治療介入を行うバイオハイブリッドプラットフォームである。 Robotic right ventricle is a biohybrid platform that simulates right ventricular function in (patho)physiological conditions and intervention
Manisha Singh,Jean Bonnemain,Caglar Ozturk,Brian Ayers,Mossab Y. Saeed,Diego Quevedo-Moreno,Meagan Rowlett,Clara Park,Yiling Fan,Christopher T. Nguyen & Ellen T. Roche
Nature Cardiovascular Research Published:08 December 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44161-023-00387-8
Abstract
The increasing recognition of the right ventricle (RV) necessitates the development of RV-focused interventions, devices and testbeds. In this study, we developed a soft robotic model of the right heart that accurately mimics RV biomechanics and hemodynamics, including free wall, septal and valve motion. This model uses a biohybrid approach, combining a chemically treated endocardial scaffold with a soft robotic synthetic myocardium. When connected to a circulatory flow loop, the robotic right ventricle (RRV) replicates real-time hemodynamic changes in healthy and pathological conditions, including volume overload, RV systolic failure and pressure overload. The RRV also mimics clinical markers of RV dysfunction and is validated using an in vivo porcine model. Additionally, the RRV recreates chordae tension, simulating papillary muscle motion, and shows the potential for tricuspid valve repair and replacement in vitro. This work aims to provide a platform for developing tools for research and treatment for RV pathophysiology.