2024-06-04 アリゾナ大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.arizona.edu/news/squirreling-it-away-unraveling-food-hoarding-behavior-conserve-endangered-squirrels
- https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/1365-2656.14093
哺乳類における食料貯蔵行動の進化的不安定性 Evolutionary lability of food caching behaviour in mammals
Sean M Mahoney, Bret Pasch
Journal of Animal Ecology Accepted:15 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.14093
Abstract
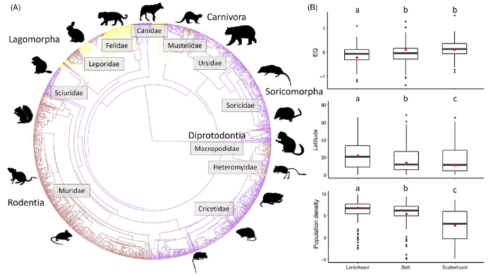
1. Food hoarding provides animals access to resources during periods of scarcity. Studies on mammalian caching indicate associations with brain size, seasonality and diet but are biased to a subset of rodents. Whether the behaviour is generalizable at other taxonomic scales and/or is influenced by other ecological factors is less understood. Population density may influence food caching due to food competition or pilferage, but this remains untested in a comparative framework.
2. Using phylogenetic analyses, we assessed the role of morphology (body and brain size), climate, diet breadth and population density on food caching behaviour evolution at multiple taxonomic scales. We also used a long-term dataset on caching behaviour of red squirrels (Tamiasciurus fremonti) to test key factors (climate and population density) on hoarding intensity.
3. Consistent with previous smaller scale studies, we found the mammalian ancestral state for food caching was larderhoarding, and scatterhoarding was derived. Caching strategy was strongly associated with brain size, population density and climate. Mammals with larger brains and hippocampal volumes were more likely to scatterhoard, and species living at higher population densities and in colder climates were more likely to larderhoard.
4. Finer-scale analyses within families, sub-families and tribes indicated that the behaviour is evolutionary labile. Brain size in family Sciuridae and tribe Marmotini was larger in scatterhoarders, but not in other tribes. Scatterhoarding in tribe Marmotini was more likely in species with lower population densities while scatterhoarding in tribe Sciurini was associated with warmer climates. Red squirrel larderhoarding intensity was positively related to population density but not climate, implicating food competition or pilferage as an important mechanism mediating caching behaviour.
5. Our results are consistent with previous smaller-scale studies on food caching and indicate the evolutionary patterns of mammalian food caching are broadly generalizable. Given the lability of caching behaviour as evidenced by the variability of our results at finer phylogenetic scales, comparative analyses must consider taxonomic scale.
6.Applying our results to conservation could prove useful as changes in population density or climate may select for different food caching strategies and thus can inform management of threatened and endangered species and their habitats.


