2024-07-02 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/key-mechanisms-identified-for-regeneration-of-neurons.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-024-01677-5
マウスアストロサイトの直接的な神経細胞初期化は、マルチスケールエピゲノムリモデリングと関連し、Yy1を必要とする Direct neuronal reprogramming of mouse astrocytes is associated with multiscale epigenome remodeling and requires Yy1
Allwyn Pereira,Jeisimhan Diwakar,Giacomo Masserdotti,Sude Beşkardeş,Tatiana Simon,Younju So,Lucía Martín-Loarte,Franziska Bergemann,Lakshmy Vasan,Tamas Schauer,Anna Danese,Riccardo Bocchi,Maria Colomé-Tatché,Carol Schuurmans,Anna Philpott,Tobias Straub,Boyan Bonev & Magdalena Götz
Nature Neuroscience Published:02 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-024-01677-5
Abstract
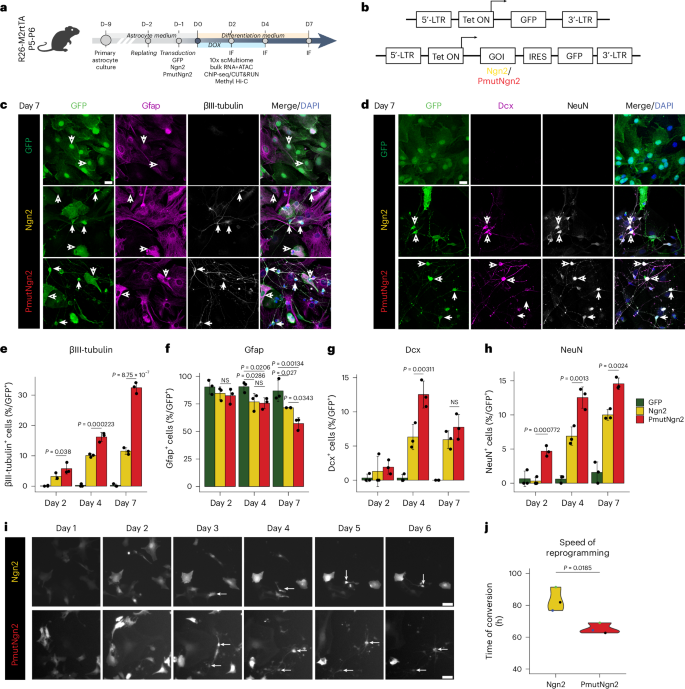
Direct neuronal reprogramming is a promising approach to regenerate neurons from local glial cells. However, mechanisms of epigenome remodeling and co-factors facilitating this process are unclear. In this study, we combined single-cell multiomics with genome-wide profiling of three-dimensional nuclear architecture and DNA methylation in mouse astrocyte-to-neuron reprogramming mediated by Neurogenin2 (Ngn2) and its phosphorylation-resistant form (PmutNgn2), respectively. We show that Ngn2 drives multilayered chromatin remodeling at dynamic enhancer–gene interaction sites. PmutNgn2 leads to higher reprogramming efficiency and enhances epigenetic remodeling associated with neuronal maturation. However, the differences in binding sites or downstream gene activation cannot fully explain this effect. Instead, we identified Yy1, a transcriptional co-factor recruited by direct interaction with Ngn2 to its target sites. Upon deletion of Yy1, activation of neuronal enhancers, genes and ultimately reprogramming are impaired without affecting Ngn2 binding. Thus, our work highlights the key role of interactors of proneural factors in direct neuronal reprogramming.