2024-10-28 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-lung-pathogen-s-dilemma-infect-or-resist-antibio/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01842-3
緑膿菌は、気道感染時に粘膜コロニー形成と抗生物質耐性の間で適応力のトレードオフに直面している Pseudomonas aeruginosa faces a fitness trade-off between mucosal colonization and antibiotic tolerance during airway infection
Lucas A. Meirelles,Evangelia Vayena,Auriane Debache,Eric Schmidt,Tamara Rossy,Tania Distler,Vassily Hatzimanikatis & Alexandre Persat
Nature Microbiology Published:25 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-024-01842-3
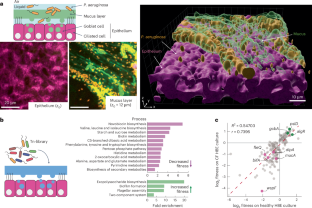
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa frequently causes antibiotic-recalcitrant pneumonia, but the mechanisms driving its adaptation during human infections remain unclear. To reveal the selective pressures and adaptation strategies at the mucosal surface, here we investigated P. aeruginosa growth and antibiotic tolerance in tissue-engineered airways by transposon insertion sequencing (Tn-seq). Metabolic modelling based on Tn-seq data revealed the nutritional requirements for P. aeruginosa growth, highlighting reliance on glucose and lactate and varying requirements for amino acid biosynthesis. Tn-seq also revealed selection against biofilm formation during mucosal growth in the absence of antibiotics. Live imaging in engineered organoids showed that biofilm-dwelling cells remained sessile while colonizing the mucosal surface, limiting nutrient foraging and reduced growth. Conversely, biofilm formation increased antibiotic tolerance at the mucosal surface. Moreover, mutants with exacerbated biofilm phenotypes protected less tolerant but more cytotoxic strains, contributing to phenotypic heterogeneity. P. aeruginosa must therefore navigate conflicting physical and biological selective pressures to establish chronic infections.


