2025-03-11 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202503/t20250312_903715.shtml
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adq4266
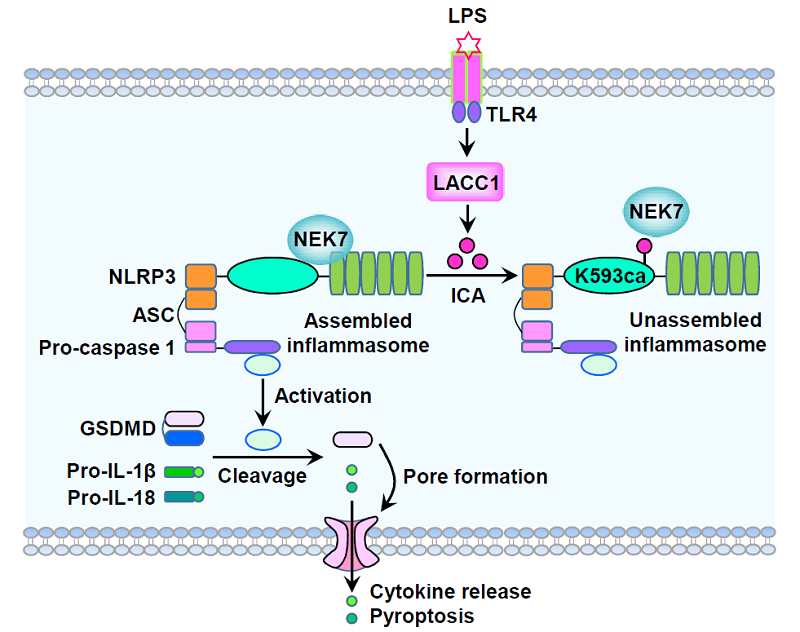
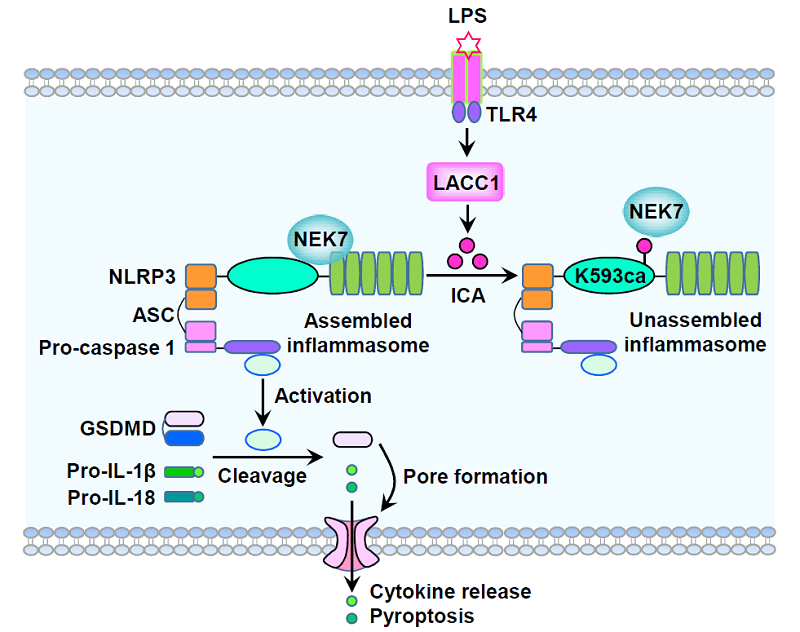
イソシアン酸を介したNLRP3のカルバモイル化は、NLRP3とNEK7の相互作用を低下させ、インフラマソームの活性化を制限する Isocyanic acid–mediated NLRP3 carbamoylation reduces NLRP3-NEK7 interaction and limits inflammasome activation
Zhenxing Zhang, Chao Chen, Caiyun Liu, Pengkai Sun, […], and Xinjian Li
Science Advances Published:7 Mar 2025

Abstract
Isocyanic acid, as a reactive metabolite synthesized by the enzyme LACC1, can carbamoylate the ε-amino group of lysine residues in proteins. However, the role of isocyanic acid in inflammatory response remains elusive. Herein, we reveal that lipopolysaccharide stimulation increases LACC1-dependent isocyanic acid production, which attenuates inflammation by limiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages primed with lipopolysaccharide for 8 hours. Mechanistically, isocyanic acid directly carbamoylates NLRP3 at lysine-593 to disrupt NLRP3-NEK7 interaction, a key step in assembly of active NLRP3 inflammasome. Abrogation of isocyanic acid biosynthesis by LACC1/Lacc1 knockout or expression of K593 carbamoylation (K593ca)–deficient NLRP3 mutant promotes macrophagic inflammatory response in vitro. Furthermore, Lacc1-/- mice and mice harboring K593ca-deficient NLRP3 mutation manifest exacerbated inflammatory response in vivo. Hence, our findings identify isocyanic acid as an endogenous immunoregulatory metabolite that limits NLRP3-driven inflammation and provide valuable insights into the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, governed by metabolites.