2025-03-12 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/antigenic-variation-decoding-the-mechanism-controlling-antigen-activation-in-trypanosomes.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08720-w
アフリカトリパノソーマにおける抗原発現階層のゲノム決定因子 Genomic determinants of antigen expression hierarchy in African trypanosomes
Zhibek Keneskhanova,Kirsty R. McWilliam,Raúl O. Cosentino,Anna Barcons-Simon,Atai Dobrynin,Jaclyn E. Smith,Ines Subota,Monica R. Mugnier,Maria Colomé-Tatché & T. Nicolai Siegel
Nature Published:12 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08720-w
Abstract
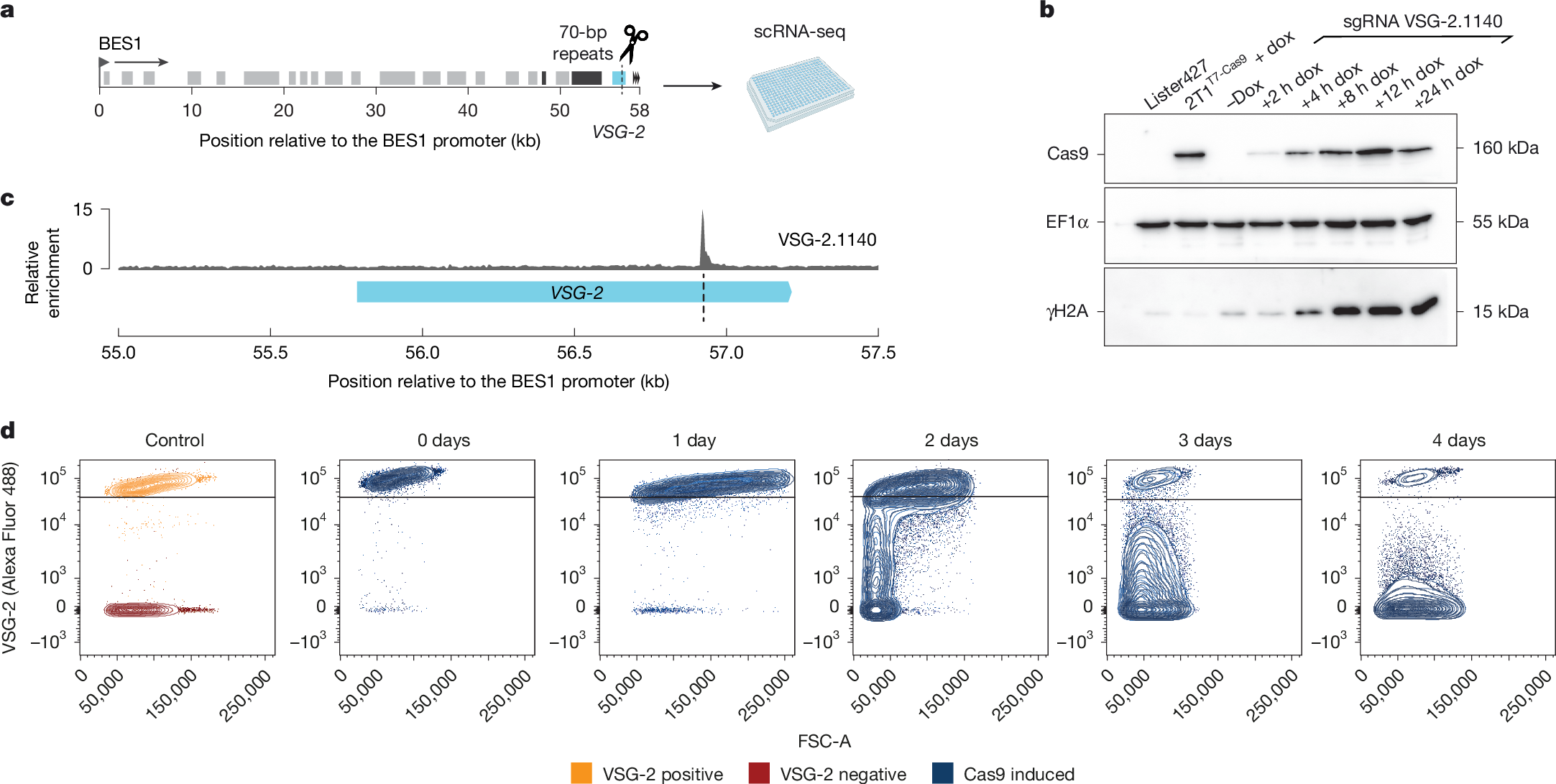
Antigenic variation is an immune evasion strategy used by many different pathogens. It involves the periodic, non-random switch in the expression of different antigens throughout an infection. How the observed hierarchy in antigen expression is achieved has remained a mystery. A key challenge in uncovering this process has been the inability to track transcriptome changes and potential genomic rearrangements in individual cells during a switch event. Here we report the establishment of a highly sensitive single-cell RNA sequencing approach for the model protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei. This approach has revealed genomic rearrangements that occur in individual cells during a switch event. Our data show that following a double-strand break in the transcribed antigen-coding gene—an important trigger for antigen switching—the type of repair mechanism and the resultant antigen expression depend on the availability of a homologous repair template in the genome. When such a template was available, repair proceeded through segmental gene conversion, creating new, mosaic antigen-coding genes. Conversely, in the absence of a suitable template, a telomere-adjacent antigen-coding gene from a different part of the genome was activated by break-induced replication. Our results show the critical role of repair sequence availability in the antigen selection mechanism. Furthermore, our study demonstrates the power of highly sensitive single-cell RNA sequencing methods in detecting genomic rearrangements that drive transcriptional changes at the single-cell level.